10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(3):861-868. doi:10.7150/ijbs.56091 This issue Cite
Research Paper
PTEN-mediated AKT/β-catenin signaling enhances the proliferation and expansion of Lgr5+ hepatocytes
1. School of Pharmaceutical Sciences (Shenzhen), Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China.
2. Medical Key Laboratory of Health Toxicology of Shenzhen, Shenzhen Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 518054, Shenzhen, China.
* These authors are the first authors of this paper.
Abstract
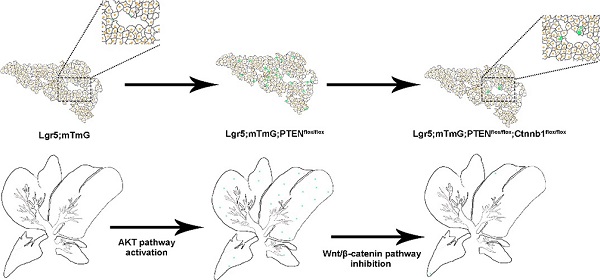
Rationale: Compelling evidence suggests that Lgr5+ hepatocytes repair liver damage by promoting the regeneration of hepatocytes and ductal cells in the case of liver injury. The PTEN-mediated AKT/β-catenin signaling plays a key role in the regulation of innate immune regulation in the liver. However, the signaling pathways that control Lgr5+ hepatocyte proliferation in the liver remain unclear.
Methods: In order to assess the involvement of PTEN-mediated AKT/β-catenin signaling in the expansion of Lgr5+ hepatocytes upon liver injuries, the Lgr5-CreER; Rosa-mTmG lineage tracing system was used to target Lgr5+ hepatocytes.
Results: The tracing of Lgr5+ hepatocytes showed that PTEN deletion and β-catenin activation significantly promoted the proliferation of Lgr5+ hepatocytes. In converse, the simultaneous inhibition of PTEN and β-catenin limited Lgr5+ hepatocyte proliferation in the liver. Our findings provide an insight into understanding how PTEN-mediated AKT/β-catenin signaling regulates the proliferation of Lgr5+ hepatocytes.
Conclusion: The outcomes can improve the application potential of Lgr5+ hepatocytes in the treatment of liver injury diseases and provide a new treatment option for liver cancer.
Keywords: AKT/β-catenin, Lgr5, hepatocyte, proliferation, liver regeneration.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact