10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(4):1061-1078. doi:10.7150/ijbs.57168 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Identification of low-dose radiation-induced exosomal circ-METRN and miR-4709-3p/GRB14/PDGFRα pathway as a key regulatory mechanism in Glioblastoma progression and radioresistance: Functional validation and clinical theranostic significance
1. Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, People's Republic of China.
2. Department of Radiation Therapy, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, People's Republic of China.
3. Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, People's Republic of China.
4. Department of Pharmacy and Internal Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, People's Republic of China.
5. Department of Radiation Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, People's Republic of China.
Abstract
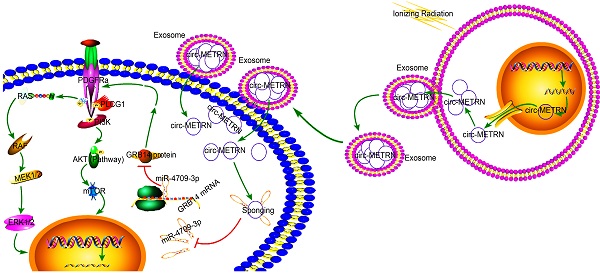
Glioblastoma is a central nervous malignancy with a very poor prognosis. This study attempted to explore the role of exosomes induced by low-dose radiation-induced (ldrEXOs) and ldrEXOs-derived circ-METRN in glioblastoma progression and radioresistance at the molecular, cellular, animal, and clinical levels. Results in the present study revealed that low-dose radiation stimulated the secretion of ldrEXOs which delivered high levels of circ-METRN. And circ-METRN-abundant ldrEXOs increased the expression of γ-H2AX, indicating an efficient DNA damage-repair process in glioblastoma cells. The ldrEXOs-derived circ-METRN enhanced the glioblastoma progression and radioresistance via miR-4709-3p/GRB14/PDGFRα pathway. Up-regulating PDGFRα can rescue the tumor-promoting function of ldrEXOs in groups previously treated with inhibition of GRB14. Additionally, in-vivo experiments revealed that treatments with ldrEXOs promoted the growth of xenografted tumors and shortened the survival period. Furthermore, clinical researches indicated that circ-METRN may be transported into the bloodstream by exosomes in the early stages of fractionated radiotherapy. It has important clinical values to detect the serum exosomal circ-METRN in the early stage of radiotherapy, which is not only conducive to predict radioresistance and prognosis but also to assist MRI diagnosis in detecting the very early recurrence of glioblastoma. In summary, this study reveals for the first time that low-dose radiation-induced exosomal circ-METRN plays an oncogenic role in glioblastoma progression and radioresistance through miR-4709-3p/GRB14/PDGFRα pathway, providing mechanistic insights into the roles of circRNAs and a valuable marker for therapeutic targets in glioblastoma.
Keywords: glioblastoma, low-dose radiation, exosome, circ-METRN, progression

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact