10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(7):1613-1628. doi:10.7150/ijbs.59559 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Upregulation of ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 5 facilitates Prostate Cancer progression and Enzalutamide resistance via the CDK1-mediated AR Ser81 Phosphorylation Pathway
Institute of Urology, Peking University. Department of Urology, Peking University First Hospital. National Urological Cancer Center of China, Beijing, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
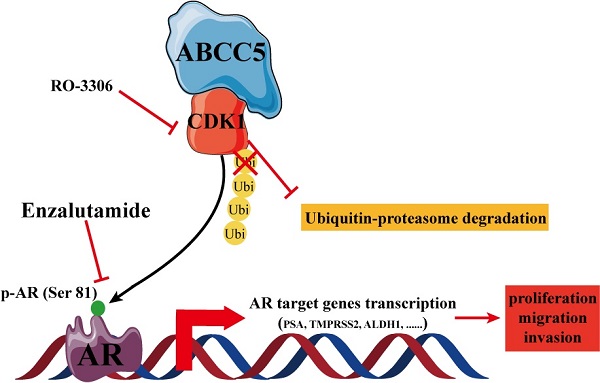
The treatment of advanced prostate cancer, castration-resistant prostate cancer, remains challenging. The mechanisms of action of ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 5 (ABCC5) in prostate cancer and its relationship with drug resistance are still unclear. Expression and prognostic analyses of ABCC5 were performed through bioinformatic methods and immunohistochemistry analyses in multiple public databases as well as in our own prostate cancer cohort. The biological function of ABCC5 in prostate cancer cells was evaluated by in vitro and in vivo cell proliferation and migration and invasion assays. The regulation of CDK1 by ABCC5 was determined via RT-qPCR, western blots, and immunofluorescence. ABCC5 was significantly overexpressed in prostate cancer and positively associated with unfavorable clinicopathological features and prognosis. Upregulation of ABCC5 could enhance the cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, ABCC5 exerts a protumor effect by binding to and inhibiting the protein degradation of CDK1, which promotes the phosphorylation of AR at Ser81 by CDK1 and activates the transcriptional activity of AR on target genes. Moreover, the addition of a CDK1 inhibitor or knockdown of CDK1 significantly improved the efficacy of enzalutamide on prostate cancer cells. The ABCC5-CDK1-AR regulatory pathway could be a potential therapeutic target for advanced prostate cancer, especially castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), to enhance the therapeutic effect of enzalutamide.
Keywords: Castration-resistant prostate cancer, ABCC5, CDK1, AR, enzalutamide

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact