10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(7):1716-1730. doi:10.7150/ijbs.56694 This issue Cite
Research Paper
NDRG1 regulates Filopodia-induced Colorectal Cancer invasiveness via modulating CDC42 activity
1. Department of General Surgery, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
2. Shanghai Minimally Invasive Surgery Center, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
3. Department of Surgery, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Gastric Neoplasms, Shanghai Institute of Digestive Surgery, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.
*First authors with equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
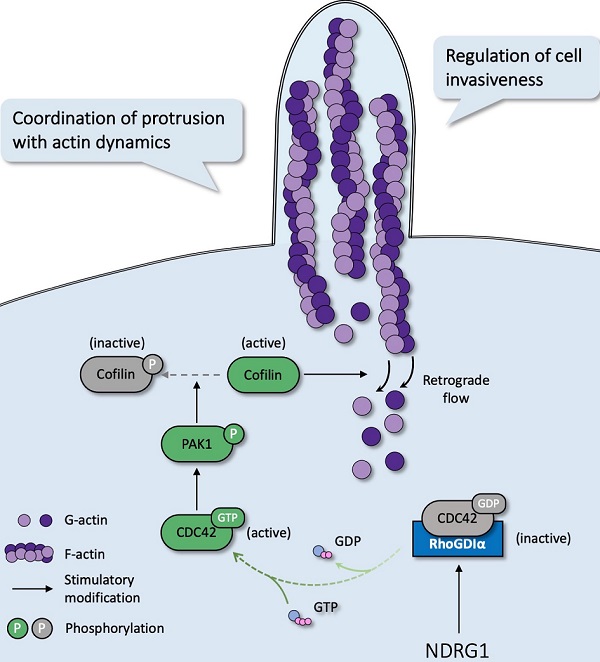
N-myc downstream regulated gene-1 (NDRG1) has been identified as a putative metastasis suppressor gene and proved to be a key player in cancer spreading and proliferation in our previous work. However, the effects of NDRG1 on tumor invasion and the mechanisms behind it are rarely understood. Here we provided in silico evidence that NDRG1 plays a crucial role in actin reorganization in colorectal cancer (CRC). Through in vitro experiments, we next observed filopodia formation was altered in NDRG1-modified cell lines, while cell division cycle-42 (CDC42) displayed excessive activation in NDRG1-silenced cells. Mechanistically, NDRG1 loss disrupts the binding between RhoGDIα and CDC42 and triggers the activation of CDC42 and the downstream cascades PAK1/Cofilin, thereby promotes the formation of filopodia and invasiveness of CRC. The knockdown of NDRG1 led to enhanced dissemination of CRC cells in vivo and correlates with active CDC42 expression. Using clinical sample analysis, we found an elevated level of active CDC42 in patients with advanced T stage, and it was negatively related to NDRG1 expression. In sum, these results uncover a mechanism utilized by NDRG1 to regulate CDC42 activity in coordinating cytoskeleton reorganization, which was crucial in cancer invasion.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, NDRG1, cytoskeleton, invasion, CDC42

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact