10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(8):1953-1962. doi:10.7150/ijbs.58135 This issue Cite
Research Paper
GABAB receptor inhibits tumor progression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the regulation of Hippo/YAP1 pathway in colorectal cancer
1. Department of Anesthesiology, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center.
2. Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China.
3. Department of Anesthesiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University; Cancer Center, ZhongShan Hospital, Fudan University; 180# Feng-Lin Road, Shanghai, 200032, China.
4. Fudan Zhangjiang Institute, Shanghai 201203, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
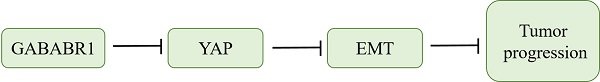
Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Type B Receptor (GABABR) plays essential roles in tumor progression. However, the function of GABABR in colorectal cancer (CRC) needs further clarification. As the main part of GABABR, GABABR1 expression was identified significantly lower in tumor tissues than those in non-tumor normal tissues and that CRC patients with high GABABR1 expression lived longer. Further studies indicated that knockdown of GABABR1 elevated CRC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Furthermore, knockdown of GABABR1 activated the expression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related proteins N-cadherin and Vimentin, whereas decrease the protein level of E-cadherin. In addition, activation of Hippo/YAP1 signaling contributes to the GABABR1 down-regulation promoted proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT in CRC cells. At last, we verified the contribution of Hippo/YAP1 signaling in the GABABR1 down-regulation impaired biological phenotype of colon cancer cells in vivo. In summary, these data indicate that GABABR1 impairs the migration and invasion of CRC cells by inhibiting EMT and the Hippo/YAP1 pathway, suggesting that GABABR1 could be a potential therapeutic target for CRC.
Keywords: Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Type B Receptor, proliferation, migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, YAP

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact