Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(10):2561-2575. doi:10.7150/ijbs.58715 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Celastrol ameliorates vascular neointimal hyperplasia through Wnt5a-involved autophagy
1. School of Pharmacy, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, China.
2. Division of Stem Cell Regulation and Application, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, China.
3. Institue of Innovation and Applied Research in Chinese Medicine, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, Hunan, China.
Abstract
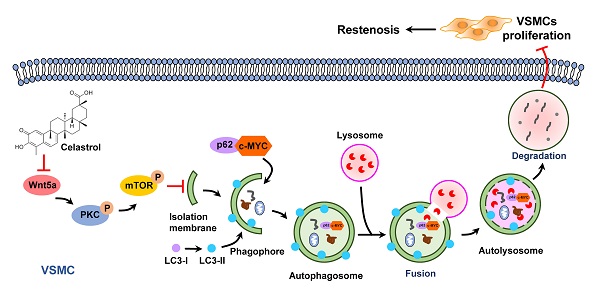
Neointimal hyperplasia caused by the excessive proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) is the pathological basis of restenosis. However, there are few effective strategies to prevent restenosis. Celastrol, a pentacyclic triterpene, has been recently documented to be beneficial to certain cardiovascular diseases. Based on its significant effect on autophagy, we proposed that celastrol could attenuate restenosis through enhancing autophagy of VSMCs. In the present study, we found that celastrol effectively inhibited the intimal hyperplasia and hyperproliferation of VSMCs by inducing autophagy. It was revealed that autophagy promoted by celastrol could induce the lysosomal degradation of c-MYC, which might be a possible mechanism contributing to the reduction of VSMCs proliferation. The Wnt5a/PKC/mTOR signaling pathway was found to be an underlying mechanism for celastrol to induce autophagy and inhibit the VSMCs proliferation. These observations indicate that celastrol may be a novel drug with a great potential to prevent restenosis.
Keywords: celastrol, vascular smooth muscle cells, neointimal formation, autophagy, restenosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact