10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(12):3118-3132. doi:10.7150/ijbs.59195 This issue Cite
Research Paper
NCTD Prevents Renal Interstitial Fibrosis via Targeting Sp1/lncRNA Gm26669 Axis
1. Department of Nephrology, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410011, China.
2. Key laboratory of kidney Disease and Blood Purification in Hunan Province, Changsha, Hunan 410011, China.
*Jiao Tian and Zheng Xiao contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
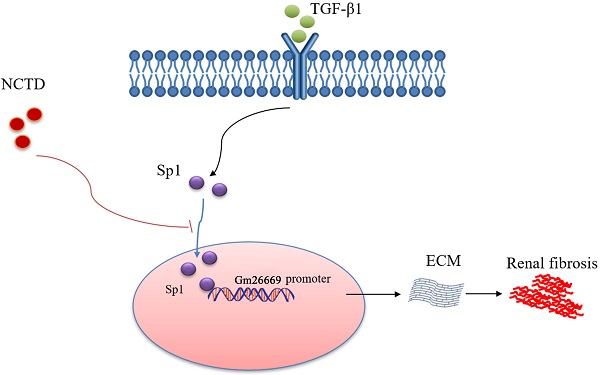
In our previous study, we demonstrated that norcantharidin (NCTD) is a potential therapeutic agent for renal interstitial fibrosis (RIF). Recently, we found that lncRNA Gm26669 (Gm26669) contributed to the development of RIF and could be regulated by NCTD. However, the upstream mechanisms of Gm26669 and whether the anti-RIF effects of NCTD are related to its regulatory action on Gm26669 remain unclear. Our bioinformatics analysis indicated that special protein1 (Sp1), a transcription factor, may bind to the promoter of Gm26669. In the present study, we observed a significant increase in the nuclear translocation of Sp1 using both in vivo and in vitro models of RIF. Furthermore, the knockdown of Sp1 inhibited the expression of collagen type I (CoL-I) and fibronectin (Fn). Mechanistically, Sp1 promoted the expression levels of CoL-I and Fn by directly binding to the promoter of Gm26669 to elevate its expression level. Moreover, we found that NCTD alleviated RIF by inhibiting Gm26669 and the nuclear translocation of Sp1. Collectively, above results suggested that NCTD might prevent RIF via targeting the Sp1/Gm26669 axis, thus providing a new theoretical basis for the clinical application of NCTD in the treatment of RIF.
Keywords: norcantharidin, special protein 1, lncRNA Gm26669, nuclear translocation, renal interstitial fibrosis

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact