10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(13):3281-3287. doi:10.7150/ijbs.60782 This issue Cite
Review
CD47/SIRPα pathway mediates cancer immune escape and immunotherapy
1. Department of Oncology, the Affiliated Wujin Hospital, Jiangsu University, Changzhou, Jiangsu Province, 213017, the People's Republic of China.
2. School of Life Sciences, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu Province, 212013, the People's Republic of China.
3. Department of Oncology, the Wujin Clinical College of Xuzhou Medical University, Jiangsu Province, 212017, the People's Republic of China.
Abstract
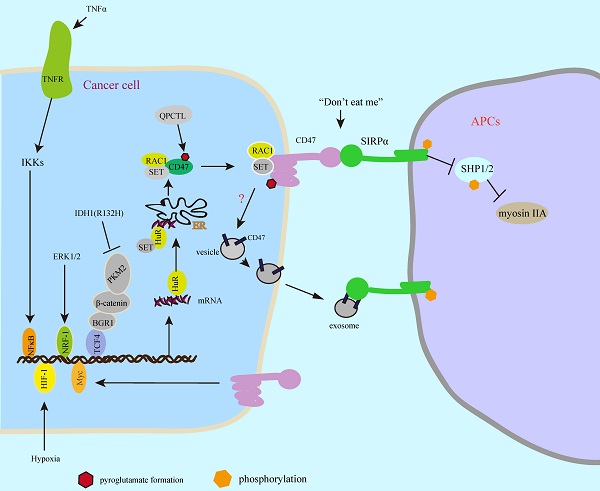
The adaptive immune checkpoints such as PD-1(programmed death-1)/PD-L1 (programmed death-ligand 1) play an important role in cancer immunotherapy, whereas increasing evidence suggests that cancer cell evades immune surveillance by innate immune checkpoints such as SIRPα (signal-regulatory protein α)/CD47 (cluster of differentiation 47). In multiple types of cancer cells and solid tumor tissues, highly expressed CD47 protein level has been observed, which is triggered by some transcription factors including NFκB, Myc, and HIF. As a transmembrane protein, the binding of CD47 to SIRPα ligand on phagocytes results in phagocytosis resistance and cancer cell immune escape. In contrast, CD47-SIRPα interaction blockade enhances cancer cell clearance by phagocytes such as macrophages and dendritic cells (DCs) to activate an innate immune response, whereas this process could promote antigen cross-presentation by antigen present cells (APCs) leading to T cell priming, consequently, activates an adaptive antitumor immune response. In this review, we discussed the current SIRPα-CD47 axis-mediated cancer cell immune escape and immunotherapy, which could provide an effective antitumor strategy by the innate and adaptive immune response.
Keywords: CD47, SIRPα, immune escape, innate immune response, adaptive immune response, cancer immunotherapy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact