10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(14):3689-3701. doi:10.7150/ijbs.62571 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived exosomal miR-3656 promotes the development and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via the ACAP2/PI3K-AKT signaling pathway
1. Department of Cell Biology, College of Life Science and Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, P. R. China
2. National Engineering Research Center of Genetic Medicine, Guangzhou 510632, P. R. China
3. Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Bioengineering Medicine, Guangzhou 510632, P. R. China
4. Guangdong Provincial biotechnology drug & Engineering Technology Research Center, Guangzhou 510632, P. R. China
5. Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute, Shandong First Medical University and Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan, P. R. China
6. Cancer Center of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510090, P. R. China
7. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine, University of California Davis, Sacramento, California, USA
8. Oncology Department, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510080, P. R. China
9. Guangdong Provincial Engineering Research Center for Precise Therapy of Esophageal Cancer, Guangzhou 510080, P. R. China
10. Department of Clinical Oncology, University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, P. R. China
*These authors contributed equally to this work and share first authorship.
Abstract
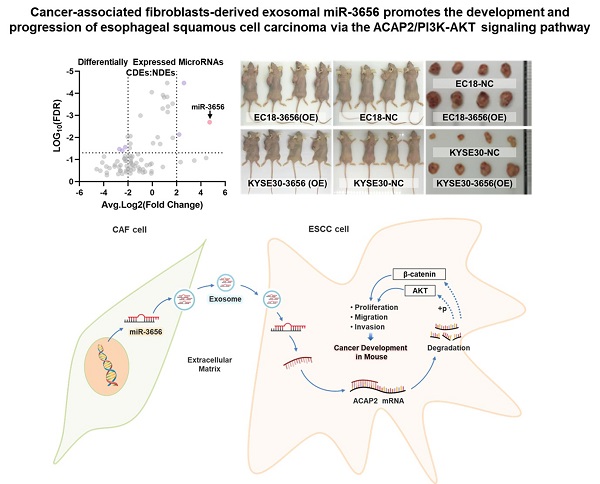
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is one of the most common gastrointestinal tumors, accounting for almost half a million deaths per year. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are the major constituent of the tumor microenvironment (TME) and dramatically impact ESCC progression. Recent evidence suggests that exosomes derived from CAFs are able to transmit regulating signals and promote ESCC development. In this study, we compared different the component ratios of miRNAs in exosomes secreted by CAFs in tumors and with those from normal fibroblasts (NFs) in precancerous tissues. The mRNA level of hsa-miR-3656 was significantly upregulated in the former exosomes. Subsequently, by comparing tumor cell development in vitro and in vivo, we found that the proliferation, migration and invasion capabilities of ESCC cells were significantly improved when miR-3656 was present. Further target gene analysis confirmed ACAP2 was a target gene regulated by miR-3656 and exhibited a negative regulatory effect on tumor proliferation. Additionally, the downregulation of ACAP2 triggered by exosomal-derived miR-3656 further promotes the activation of the PI3K/AKT and β-catenin signaling pathways and ultimately improves the growth of ESCC cells both in vitro and in xenograft models. These results may represent a potential therapeutic target for ESCC and provide a new basis for clinical treatment plans.
Keywords: Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC), Cancer-associated Fibroblast (CAF), Exosome, MicroRNA miR-3656, ACAP2

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact