10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(14):3936-3953. doi:10.7150/ijbs.63732 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Lrp6 Genotype affects Individual Susceptibility to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Silibinin Therapeutic Response via Wnt/β-catenin-Cyp2e1 Signaling
1. Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan, China.
2. Institute of Clinical Pharmacology, Central South University, Changsha 410078, Hunan, China.
3. Engineering Research Center of Applied Technology of Pharmacogenomics, Ministry of Education, 110 Xiangya Road, Changsha 410078, P. R. China.
4. National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, 87 Xiangya Road, Changsha 410008, Hunan, P.R. China.
5. Department of Pharmacy, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan, China.
6. Department of gastroenterology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan, China.
7. Department of Hepatology and Infectious Diseases, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, Hunan, China.
8. Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Maryland 21201. USA.
Abstract
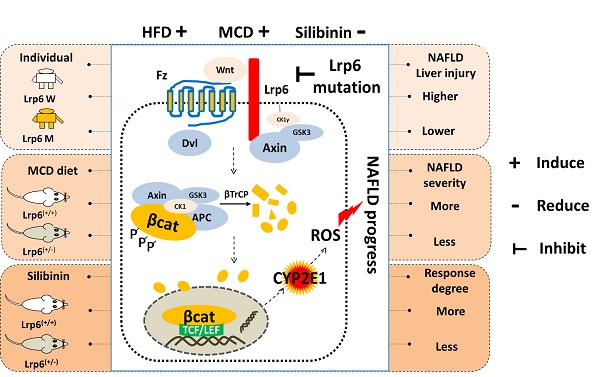
Background: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a serious threat to human health worldwide, with a high genetic susceptibility. Rs2302685, a functional germline variant of LRP6, has been recently found to associate with NAFLD risk. This study was aimed to clarify the underlying mechanism associated with rs2302685 risk and its impact on pharmacotherapy in treatment of NAFLD.
Methods: Venous blood samples were collected from NAFLD and non-NAFLD patients for SNP genotyping by using mass spectrometry. The Lrp6-floxdel mouse (Lrp6(+/-)) was generated to model the partial function associated with human rs2302685. The liver injury and therapeutic effects of silibinin were compared between Lrp6(+/-) and Lrp6(+/+) mice received a methionine-choline deficient (MCD) diet or normal diet. The effect of Lrp6 functional alteration on Wnt/β-catenin-Cyp2e1 signaling activities was evaluated by a series of cellular and molecular assays.
Results: The T allele of LRP6 rs2302685 was confirmed to associate with a higher risk of NAFLD in human subjects. The carriers of rs2302685 had reduced level of AST and ALT as compared with the noncarriers. The Lrp6(+/-) mice exhibited a less severe liver injury induced by MCD but a reduced response to the treatment of silibinin in comparison to the Lrp6(+/+) mice, suggesting Lrp6 as a target of silibinin. Wnt/β-catenin-Cyp2e1 signaling together with ROS generation could be exacerbated by the overexpression of Lrp6, while decreased in response to Lrp6 siRNA or silibinin treatment under NAFLD modeling.
Conclusions: The Lrp6 function affects individual susceptibility to NAFLD and the therapeutic effect of silibinin through the Wnt/β-catenin-Cyp2e1 signaling pathway. The present work has provided an underlying mechanism for human individual susceptibility to NAFLD associated with Lrp6 polymorphisms as well as a rationale for the effective use of silibinin in NAFLD patients.
Keywords: low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, genotype, reactive oxygen species, cytochrome P450 2e1

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact