10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(14):4060-4072. doi:10.7150/ijbs.63305 This issue Cite
Review
The Hippo pathway: a renewed insight in the craniofacial diseases and hard tissue remodeling
1. Xiangya School of Stomatology, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China.
2. Xiangya Stomatological Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China.
3. Hunan Key Laboratory of Oral Health Research, Hunan 3D Printing Engineering Research Center of Oral Care, Hunan Clinical Research Center of Oral Major Diseases and Oral Health, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China.
4. National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on High-strength Structural Materials, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China.
5. State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
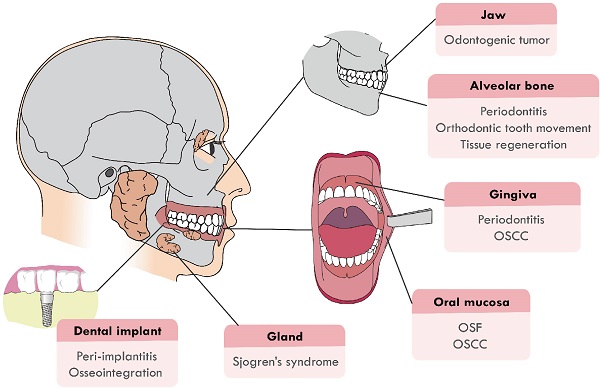
The Hippo pathway plays an important role in many pathophysiological processes, including cell proliferation and differentiation, cell death, cell migration and invasion. Because of its extensive functions, Hippo pathway is closely related to not only growth and development, but also many diseases, including inflammation and cancer. In this study, the role of Hippo pathway in craniofacial diseases and hard tissue remodeling was reviewed, in attempting to find new research directions.
Keywords: Hippo signaling pathway, YAP, TAZ, periodontal diseases, oral submucous fibrosis, craniofacial diseases

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact