10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(15):4154-4164. doi:10.7150/ijbs.65066 This issue Cite
Review
Current Advancement on the Dynamic Mechanism of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
1. Department of General Surgery, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
2. Beijing Key Laboratory of Cancer Invasion and Metastasis Research, Beijing, China.
3. National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Diseases, Beijing, China.
4. Beijing Institute of Clinical Medicine, Beijing, China.
5. Department of Hematology, Fuxing Hospital, Eighth Clinical Medical College, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
6. Department of Anesthesiology, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
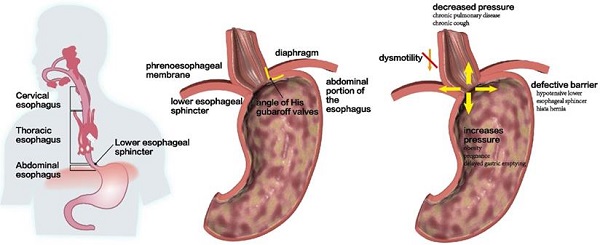
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common clinical disease associated with upper gastrointestinal motility disorders. Recently, with improvements in living standards and changes in lifestyle and dietary habits, the incidence of GERD has been increasing yearly. However, the mechanism of GERD has not been fully elucidated due to its complex pathogenesis, and this had led to unsatisfactory therapeutic outcomes. Currently, the occurrence and development of GERD involve multiple factors. Its pathogenesis is mainly thought to be related to factors, such as lower esophageal sphincter pressure, transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation, crural diaphragmatic dysfunction, hiatus hernia, and impaired esophageal clearance. Therefore, explaining the pathogenesis of GERD more clearly and systematically, exploring potential and effective therapeutic targets, and choosing the best treatment methods have gradually become the focus of scholars' attention. Herein, we reviewed current advancements in the dynamic mechanism of GERD to better counsel patients on possible treatment options.
Keywords: gastroesophageal reflux disease, dynamic mechanism, anti-reflux barrier disruption, esophageal clearance impaired, advancement

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact