Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(15):4409-4425. doi:10.7150/ijbs.64533 This issue Cite
Research Paper
PiRNA-63049 inhibits bone formation through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
1. Department of Spine Surgery, the Second Clinical Medical College, Jinan University (Shenzhen People's Hospital), Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Musculoskeletal Tissue Reconstruction and Function Restoration, Shenzhen 518020, China.
2. The First Affiliated Hospital, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510630, China.
3. The First Affiliated Hospital, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China.
4. School of Medicine, Southern University of Science and Technology, Guangdong, Provincial Key Laboratory of Cell Microenvironment and Disease Research, Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Cell Microenvironment, Shenzhen 518055, China.
5. Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 999077 China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
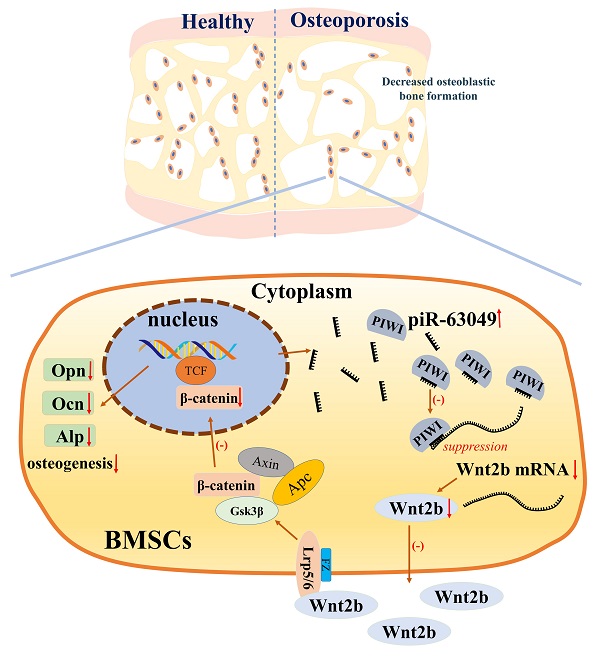
Bone remodeling is a dynamic process between bone formation mediated by osteoblasts and bone resorption mediated by osteoclasts. Disrupted bone remodeling is a key factor in postmenopausal osteoporosis, a metabolic disorder characterized by deteriorated bone microarchitecture and increased risk of fracture. Recent studies have shown that piwi-binding RNA (piRNA) is involved in the pathogenesis of certain diseases at the post-transcriptional level. Here, we analyzed piRNA-63049 (piR-63049), which may play an essential role in bone remodeling. The expression of piR-63049 significantly increased in both bone tissues and plasma of osteoporotic rats and postmenopausal osteoporotic patients. Overexpressing piR-63049 could inhibit the osteoblastogenesis of bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) while knocking down piR-63049 could promote the osteoblastogenesis of BMSCs through the Wnt2b/β-catenin signaling pathway. Moreover, knocking-down piR-63049 (piR-63049-antagonist) in vivo could attenuate the bone loss in ovariectomized rats by promoting bone formation. Taken together, the current study shows that piR-63049 inhibits bone formation through the Wnt2b/β-catenin signaling pathway. This novel piRNA may be a potential target to increase bone formation in bone loss disorders such as postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Keywords: Bone formation, Bone marrow stromal cells, Piwi-interacting RNAs, Wnt signaling

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact