10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(2):800-808. doi:10.7150/ijbs.65457 This issue Cite
Review
Role of RHO family interacting cell polarization regulators (RIPORs) in health and disease: Recent advances and prospects
1. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Shanghai First Maternity and Infant Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China.
2. Department of Breast Surgery, Shanghai First Maternity and Infant Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
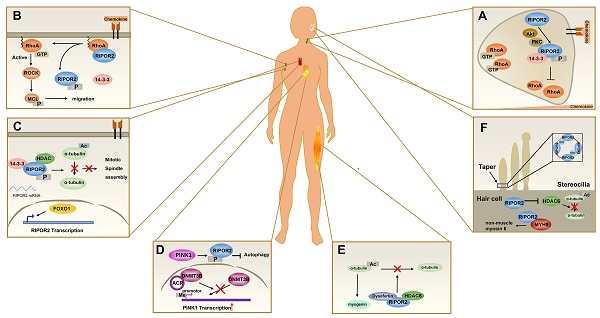
The RHO GTPase family has been suggested to play critical roles in cell growth, migration, and polarization. Regulators and effectors of RHO GTPases have been extensively explored in recent years. However, little attention has been given to RHO family interacting cell polarization regulators (RIPORs), a recently discovered protein family of RHO regulators. RIPOR proteins, namely, RIPOR1-3, bind directly to RHO proteins (A, B and C) via a RHO-binding motif and exert suppressive effects on RHO activity, thereby negatively influencing RHO-regulated cellular functions. In addition, RIPORs are phosphorylated by upstream protein kinases under chemokine stimulation, and this phosphorylation affects not only their subcellular localization but also their interaction with RHO proteins, altering the activation of RHO downstream targets and ultimately impacting cell polarity and migration. In this review, we provide an overview of recent studies on the function of RIPOR proteins in regulating RHO-dependent directional movement in immune responses and other pathophysiological functions.
Keywords: RIPOR1, RIPOR2, RIPOR3, RHO GTPase, RHOA, RHOC, 14-3-3 protein, polarization, migration

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact