ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(4):1539-1554. doi:10.7150/ijbs.67842 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Pantothenate Kinase 1 Inhibits the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Negatively Regulating Wnt/β-catenin Signaling
1. Department of Oncology, Xiangya Cancer Center, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China.
2. NHC Key Laboratory of Pulmonary Immune-related Diseases, Guizhou Provincial People's Hospital, Guiyang 550002, China.
3. Hunan Cancer Hospital, The Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha, 410013, China.
4. Faculty of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery, The First Medical Center of Chinese People's Liberation Army (PLA), General Hospital, Beijing, China.
5. State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, National Clinical Research Center for Respiratory Disease, Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Health, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510120, China.
6. Department of Infectious Disease, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China.
7. Tianjin Key Laboratory of Lung Cancer Metastasis and Tumor Microenvironment, Tianjin Lung Cancer Institute, Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin, P. R. China.
8. Key Laboratory of Molecular Radiation Oncology Hunan Province, Changsha 410008, China.
9. National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, Department of Geriatrics, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410008, China
10. Hunan International Science and Technology Collaboration Base of Precision Medicine for Cancer, Changsha 410008, China.
11. Center for Molecular Imaging of Central South University, Xiangya Hospital, Changsha 410008, China.
12. Department of Hepatic Surgery I (Ward I), Shanghai Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital, Shanghai 200438, China.
Abstract
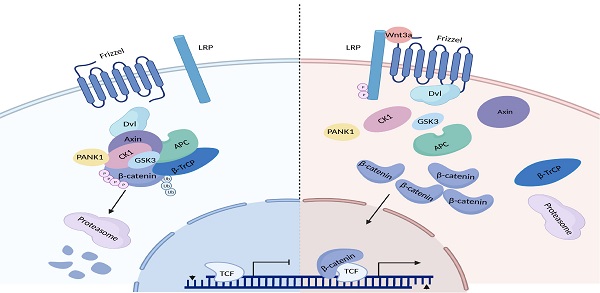
Hyperactivation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling has been reported in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the mechanisms underlying the hyperactivation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling are incompletely understood. In this study, Pantothenate kinase 1 (PANK1) is shown to be a negative regulator of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Downregulation of PANK1 in HCC correlates with clinical features. Knockdown of PANK1 promotes the proliferation, growth and invasion of HCC cells, while overexpression of PANK1 inhibits the proliferation, growth, invasion and tumorigenicity of HCC cells. Mechanistically, PANK1 binds to CK1α, exerts protein kinase activity and cooperates with CK1α to phosphorylate N-terminal serine and threonine residues in β-catenin both in vitro and in vivo. Additionally, the expression levels of PANK1 and β-catenin can be used to predict the prognosis of HCC. Collectively, the results of this study highlight the crucial roles of PANK1 protein kinase activity in inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling, suggesting that PANK1 is a potential therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, Wnt/β-catenin signaling, PANK1, protein kinase activity, CK1α

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact