10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(4):1594-1611. doi:10.7150/ijbs.68873 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Atractylenolide III ameliorates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by activating Hepatic Adiponectin Receptor 1-Mediated AMPK Pathway
1. Laboratory of Cellular Immunity, Shuguang Hospital, Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China.
2. Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China.
3. School of Life Science and Technology and Shanghai Institute for Advanced Immunochemical Studies, Shanghai Tech University, Shanghai, China.
4. Department of Hepatopathy, Shuguang Hospital, Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China.
#These authors made equal contributions to this work.
Abstract
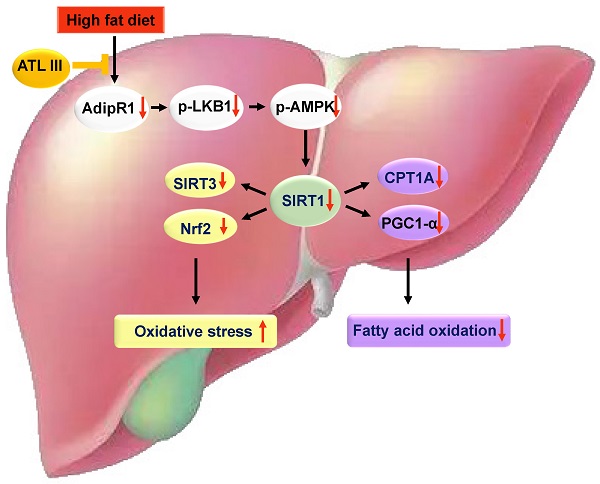
Background: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most frequent cause of chronic liver diseases worldwide. At present, there are no effective pharmacological therapies for NAFLD except lifestyle intervention-mediated weight loss. Atractylenolide III (ATL III), the major bioactive component found in Atractylode smacrocephala Koidz, has been shown to exert anti-oxidant, anti-tumor, anti-allergic response, anti-bacterial effects and cognitive protection. Here we investigate the therapeutic potential and underlying mechanisms of ATL III for the treatment of NAFLD.
Methods: Male C57BL/6J mice were fed a high-fat diet (HFD) and treated with ATL III. Lipid accumulation was analyzed by Oil Red O staining in liver tissues and free fatty acids (FFAs)-treated hepatocytes. AMP-activated protein (AMPK) and sirtuin 1(SIRT1) signaling pathways were inhibited by Compound C and EX527 in vitro, respectively. Small-interfering RNA (siRNA) was used to knockdown adiponectin receptor 1 (AdipoR1) expression in HepG2 cells.
Results: ATL III treatment ameliorated liver injury and hepatic lipid accumulation in the HFD-induced NAFLD mouse model as demonstrated by that ATL III administration significantly reduced serum levels of alanine aminotransferase, glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, triglycerides, total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein. Furthermore, treatment with ATL III alleviated hepatic oxidative stress, inflammation and fibrosis in the HFD feeding model. To study the underlying mechanisms, we performed Computer Aided Design assay and found that open-formed AdipoR1 and adiponectin receptor 2 were the potential receptors targeted by ATL III. Interestingly, HFD feeding or FFAs treatment only reduced hepatic AdipoR1 expression, while such reduction was abolished by ATL III administration. In addition, in vitro treatment with ATL III activated the AdipoR1 downstream AMPK /SIRT1 signaling pathway and reduced lipid deposition in HepG2 cells, which was diminished by silencing AdipoR1. Finally, inhibition of AMPK or SIRT1, the AdipoR1 downstream signaling, abolished the protective effects of ATL III on lipid deposition and oxidative stress in FFAs-treated HepG2 cells.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that ATL III is a therapeutic drug for the treatment of NAFLD and such protective effect is mediated by activating hepatic AdipoR1-mediated AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: ATL III, AdipoR1, oxidative stress, inflammation, AMPK, SIRT1

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact