ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(4):1663-1676. doi:10.7150/ijbs.69405 This issue Cite
Research Paper
M2 Macrophage Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of MiR-186-5p Promotes Colon Cancer Progression by Targeting DLC1
Department of Gastroenterology, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, National Clinical Research Center for Digestive Disease, Beijing Digestive Disease Center, Beijing Key Laboratory for Precancerous Lesion of Digestive Disease, Beijing, 100050, P. R. China
Abstract
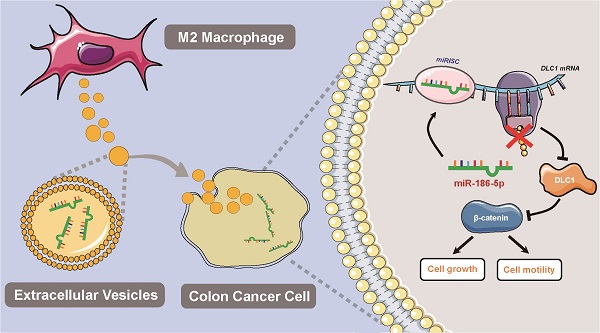
Colon cancer (CC) is one of the most common malignances in digestive tract. M2-polarized macrophages within the tumor microenvironment could facilitate CC cell growth by transferring molecules via extracellular vesicles, but the mechanisms are not fully elucidated. The current study aims to identify the possible effectors in M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles (M2-EVs) and reveal related molecular mechanisms. In our study, we validated the promotion effects of M2-EVs on the proliferation and motility of CC cells, which was found to be dependent on the EVs enclosed molecules by a mild EVs digestion assay. Then we found that miR-186-5p was enriched in M2-EVs and was responsible for the tumor promoting functions of M2-EVs. Furthermore, mechanism investigation revealed M2-EVs transferring miR-186-5p inhibited DLC1 expression by targeting its 3'UTR, and restored DLC1 successfully neutralized the tumor-promoting effects of M2-EVs transferring miR-186-5p via inhibiting the β-catenin pathway. Our study revealed that M2-EVs facilitates the growth and motility of CC cells by delivering the enclosed miR-186-5p, which directly targets DLC1 mRNAs and facilitates their degradation, which could provide a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for CC.
Keywords: Colon cancer (CC), M2 macrophage, Extracellular vesicles (EVs), miR-186-5p, DLC1

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact