10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(5):2003-2017. doi:10.7150/ijbs.69618 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dissection of Targeting Molecular Mechanisms of Aristolochic Acid-induced Nephrotoxicity via a Combined Deconvolution Strategy of Chemoproteomics and Metabolomics
1. Artemisinin research center, and Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China.
2. School of Chinese Materia Medica, and State Key Laboratory of Component-based Chinese Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China.
3. School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China.
4. Department of Urology, The Second Clinical Medical College, Jinan University (Shenzhen People's Hospital), Shenzhen, Guangdong 518020, China.
5. Center for Reproductive Medicine, Dongguan Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital, Southern Medical University, Dongguan 523125, China.
6. Central People's Hospital of Zhanjiang, Zhanjiang, Guangdong 524037, China.
7. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of New Drug Screening, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
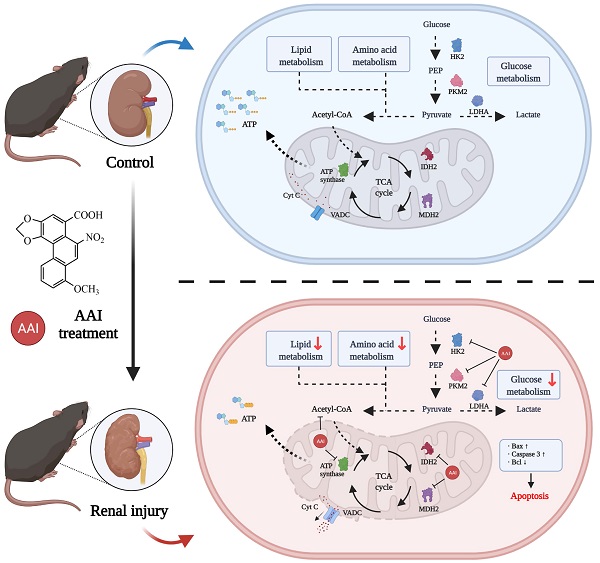
Aristolochic acid (AA), mainly derived from herbal Aristolochia and Asarum plants, was listed as a human carcinogen class I in 2002. Aristolochic acid nephropathy (AAN) is a rapidly progressive tubulointerstitial nephritis and urothelial cancer caused by AA. However, the targeting molecular mechanisms of AAs-induced nephrotoxicity are largely unclear. This study aims to dissect targeting molecular mechanisms of AA-induced nephrotoxicity. Activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) in combination with cellular thermal shift assay (CETSA) was performed to identify the AAs binding target proteins. Our data indicated that several key enzymes in the metabolic process and mitochondrial respiration including IDH2 and MDH2 (Krebs cycle), PKM and LDH (aerobic respiration), FASN (fatty acid beta-oxidation), HK2 (glucose metabolism), and ATP synthase were identified as directly binding targets of AAs. Metabolomics and oxygen consumption rate (OCR) experiments further confirmed that AAs targeting proteins disrupted metabolic biosynthesis processes and impaired mitochondrial functions. Ultimately, AAs induced renal cells apoptosis by disturbing various biological processes. Cumulatively, AAs may directly bind to key proteins involved in the metabolic process and mitochondrial homeostasis, and finally induce aristolochic acid nephropathy. Our findings provide novel insight into underlying mechanisms of AAs-induced kidney toxicity, which may help to develop therapeutic strategies for AAN.
Keywords: Aristolochic acid nephropathy, chemical proteomics, mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, metabolism

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact