10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(5):2018-2031. doi:10.7150/ijbs.69024 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hgs Deficiency Caused Restrictive Cardiomyopathy via Disrupting Proteostasis
1. State Key Laboratory of Proteomics, Beijing Proteome Research Center, National Center for Protein Sciences, Beijing Institute of Lifeomics, Beijing 100071, China.
2. Institute of Vascular Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital and Key Laboratory of Molecular Cardiovascular Sciences, Ministry of Education, Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Molecular Biology and Regulatory Peptides, Ministry of Health, Beijing 100191, China.
3. The State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology, CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 200031, China.
*These authors have contributed equally to this study and share first authorship.
Abstract
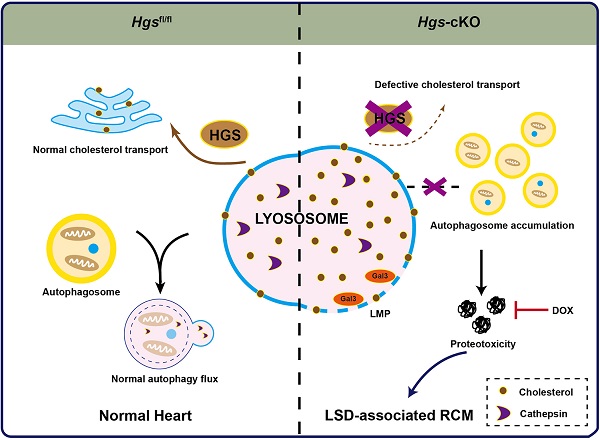
The molecular mechanisms underlying restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) are not fully understood. Hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (HGS) is a vital element of Endosomal sorting required for transport (ESCRT), which mediates protein sorting for degradation and is crucial for protein homeostasis (proteostasis) maintenance. However, the physiological function and underlying mechanisms of HGS in RCM are unexplored. We hypothesized that HGS may play vital roles in cardiac homeostasis. Cardiomyocyte-specific Hgs gene knockout mice were generated and developed a phenotype similar to human RCM. Proteomic analysis revealed that Hgs deficiency impaired lysosomal homeostasis in cardiomyocytes. Loss of Hgs disrupted cholesterol transport and lysosomal integrity, resulting in lysosomal storage disorder (LSD) with aberrant autophagosome accumulation and protein aggregation. Suppression of protein aggregation by doxycycline treatment attenuated cardiac fibrosis, and diastolic dysfunction in Hgs-knockout mice. These findings uncovered a novel physiological role of HGS in regulating cardiac lysosomal homeostasis and proteostasis, suggesting that the deficient HGS contributes to LSD-associated RCM-like cardiomyopathy.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact