Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(8):3324-3336. doi:10.7150/ijbs.71167 This issue Cite
Research Paper
KLF4 Alleviates Hypertrophic Scar Fibrosis by Directly Activating BMP4 Transcription
1. Department of Burns and Cutaneous Surgery, Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, 127 Changle West Road, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710032, China;
2. State Key Laboratory of Military Stomatology, National Clinical Research Centre for Oral Diseases, Shaanxi International Joint Research Centre for Oral Diseases, Department of Oral Anatomy and Physiology and TMD, School of Stomatology, Fourth Military Medical University, 127 Changle West Road, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710032, China
3. State Key Laboratory of Cancer Biology and National Clinical Research Centre for Digestive Diseases, Xijing Hospital of Digestive Diseases, Fourth Military Medical University, 127 Changle West Road, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710032, China
4. Department of Emergency, Xijing Hospital, Air Force Medical University, 127 Changle West Road, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710032, China
# These authors share first authorship
Abstract
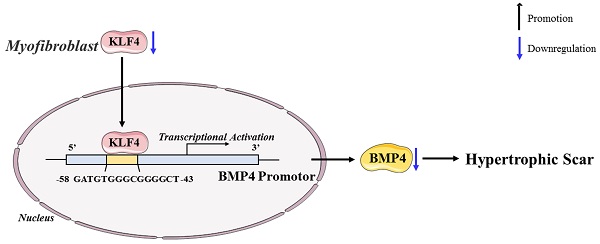
Background: Hypertrophic scars (HS) often occur after burns, surgery and extensive trauma. Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is a member of the Krüppel-like factor family, a group of conserved zinc finger transcription factors that regulate diverse cellular processes. KLF4 can participate in the regulation of fibrotic diseases in many organs, such as the lung, liver, and heart. However, the antifibrotic effect of KLF4 in skin HS remains elusive.
Result: This study observed the inhibition of KLF4 on fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. Our results revealed that KLF4 expression was decreased in HS tissue and fibroblasts. The results of KLF4 transfection confirmed its ability to alleviate the transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts both in vitro and in vivo, thereby inhibiting the development of fibrosis. In addition, ChIP assays showed that BMP4 was the target gene of KLF4 for inhibiting skin fibrosis.
Conclusions: Collectively, this evidence indicates that KLF4 is associated with BMP4 and could play an important regulatory role in HS formation by downregulating myofibroblast transdifferentiation. Our study provides a new target for the prevention and treatment of hypertrophic scars.
Keywords: Krüppel-like factor 4, Hypertrophic scar, Transcriptional activation, BMP4

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact