10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(8):3390-3404. doi:10.7150/ijbs.69833 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Dynamics of the gut-liver axis in rats with varying fibrosis severity
Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology for Infectious Diseases (Ministry of Education), Institute for Viral Hepatitis, Department of Infectious Diseases, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400010, China.
Abstract
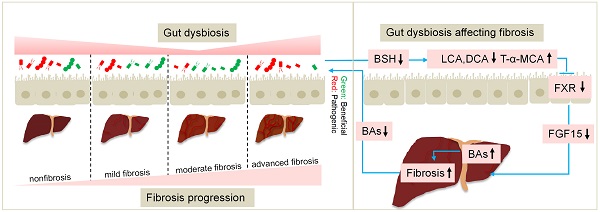
The classic carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver injury model is widely used to study the pathogenesis of fibrosis and evaluate anti-fibrosis drugs. Here, we investigated the dynamic changes in the gut microbiota, bile acids (BAs) and the gut barrier over different fibrosis severities in a CCl4-based model. 16S rDNA sequencing demonstrated that the beneficial taxon Lactobacillus was always underrepresented, and pathogens including Escherichia_Shigella, Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1, Colidextribacter, and Lachnospiraceae_UCG_010 were significantly overrepresented across liver fibrosis severities. Gut dysbiosis was more severe at the early stage of liver injury and advanced stage of fibrosis. An ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) analysis revealed that with the progress of fibrosis, unconjugated BAs in faeces were significantly decreased and conjugated BAs in serum were significantly increased. The FXR-SHP signalling pathway in the liver and ileum was statistically repressed in the fibrosis groups. Determination of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-dextran levels in plasma showed that the intestinal barrier remained relatively intact in the advanced fibrosis stage. The advances in knowledge of the gut-liver axis provided by this study yield new insights for application in research and drug evaluation.
Keywords: gut-liver axis, liver fibrosis, gut microbiota, bile acid, gut barrier

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact