10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(10):4233-4244. doi:10.7150/ijbs.70866 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Interaction between BEND5 and RBPJ suppresses breast cancer growth and metastasis via inhibiting Notch signaling
1. Medical College, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, P.R. China.
2. Department of Medical Molecular Biology, Beijing Institute of Biotechnology, Beijing 100850, P.R. China.
3. Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou, Liaoning 121001, P.R. China.
4. Department of Oncology, The fifth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100071, P.R. China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
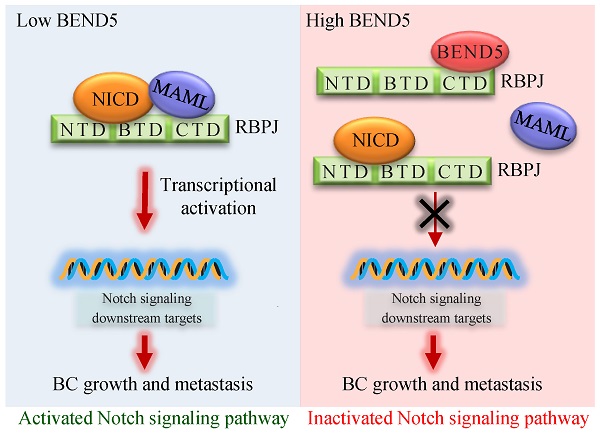
High frequent metastasis is the major cause of breast cancer (BC) mortality among women. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying BC metastasis remain largely unknown. Here, we identified six hub BC metastasis driver genes (BEND5, HSD11B1, NEDD9, SAA2, SH2D2A and TNFSF4) through bioinformatics analysis, among which BEND5 is the most significant gene. Low BEND5 expression predicted advanced stage and shorter overall survival in BC patients. Functional experiments showed that BEND5 could suppress BC growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, BEND5 inhibits Notch signaling via directly interacting with transcription factor RBPJ/CSL. BEN domain of BEND5 interacts with the N-terminal domain (NTD) domain of RBPJ, thus preventing mastermind like transcriptional coactivator (MAML) from forming a transcription activation complex with RBPJ. Our study provides a novel insight into regulatory mechanisms underlying Notch signaling and suggests that BEND5 may become a promising target for BC therapy.
Keywords: Breast cancer, metastasis, bioinformatics, BEND5, Notch signaling

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact