Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(11):4452-4465. doi:10.7150/ijbs.69882 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Deacetylation of Glutaminase by HDAC4 contributes to Lung Cancer Tumorigenesis
1. School of Basic Medical Sciences, Nanchang University, Nanchang, 330031, P. R. China.
2. School of Life Sciences, Nanchang University, Nanchang, 330031, P.R. China.
3. Jiangxi Institute of Respiratory Disease, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, 330006, P.R. China.
Abstract
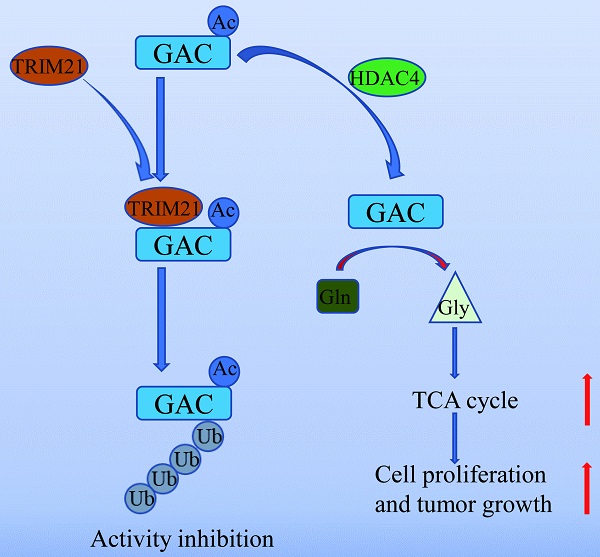
Inhibiting cancer metabolism via glutaminase (GAC) is a promising strategy to disrupt tumor progression. However, mechanism regarding GAC acetylation remains mostly unknown. In this study, we demonstrate that lysine acetylation is a vital post-translational modification that inhibits GAC activity in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We identify that Lys311 is the key acetylation site on GAC, which is deacetylated by HDAC4, a class II deacetylase. Lys311 acetylation stimulates the interaction between GAC and TRIM21, an E3 ubiquitin ligase of the tripartite motif (TRIM) family, therefore promoting GAC K63-linked ubiquitination and inhibiting GAC activity. Furthermore, GACK311Q mutation in A549 cells decreases cell proliferation and alleviates tumor malignancy. Our findings reveal a novel mechanism of GAC regulation by acetylation and ubiquitination that participates in non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis.
Keywords: glutaminase, acetylation, HDAC4, TRIM21, non-small cell lung cancer

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact