Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(12):4704-4713. doi:10.7150/ijbs.72663 This issue Cite
Review
Signaling mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein in viral infection, cell death and inflammation
1. Medical Research Center and Guangdong-Hong Kong Joint Laboratory for Immunity and Genetics of Chronic Kidney Disease, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou, China.
2. Department of Nephrology, The Third Affiliated hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
3. Departments of Medicine & Therapeutics, Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, and Lui Che Woo Institute of Innovative Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
4. The Chinese University of Hong Kong-Guangdong Academy of Sciences/Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital Joint Research Laboratory on Immunological and Genetic Kidney Diseases, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China.
Abstract
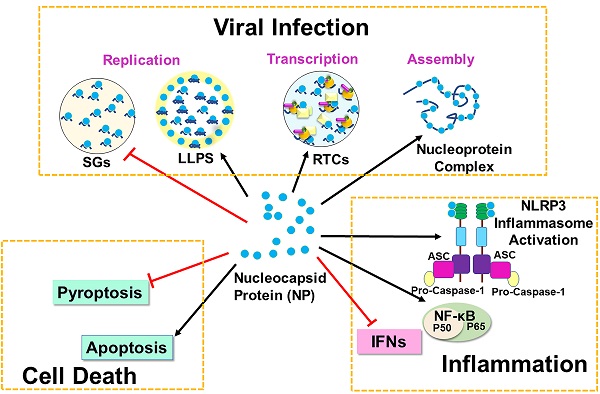
COVID-19 which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) has posed a worldwide pandemic and a major global public health threat. SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid (N) protein plays a critical role in multiple steps of the viral life cycle and participates in viral replication, transcription, and assembly. The primary roles of N protein are to assemble with genomic RNA into the viral RNA-protein (vRNP) complex and to localize to the replication transcription complexes (RTCs) to enhance viral replication and transcription. N protein can also undergo liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) with viral genome RNA and inhibit stress granules to facilitate viral replication and assembly. Besides the function in viral life cycle, N protein can bind GSDMD to antagonize pyroptosis but promotes cell death via the Smad3-dependent G1 cell cycle arrest mechanism. In innate immune system, N protein inhibits IFN-β production and RNAi pathway for virus survival. However, it can induce expression of proinflammatory cytokines by activating NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome, resulting in cytokine storms. In this review article, we are focusing on the signaling mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 N protein in viral replication, cell death and inflammation.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact