10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(14):5230-5240. doi:10.7150/ijbs.70117 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inhibition of APOE potentiates immune checkpoint therapy for cancer
1. Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China.
2. Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China.
3. Department of General Surgery, Nanjing First Hospital, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China.
4. Hepatobiliary/Liver Transplantation Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Key Laboratory of Living Donor Transplantation, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China.
5. First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China.
6. State Key Laboratory of Modern Chinese Medicine, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China.
7. Research Unit Analytical Pathology, Helmholtz Zentrum München, German Research Center for Environmental Health (GmbH), Neuherberg, Germany.
8. Department of plastic and hand surgery, University Hospital Munich, Campus Innenstadt, Germany.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
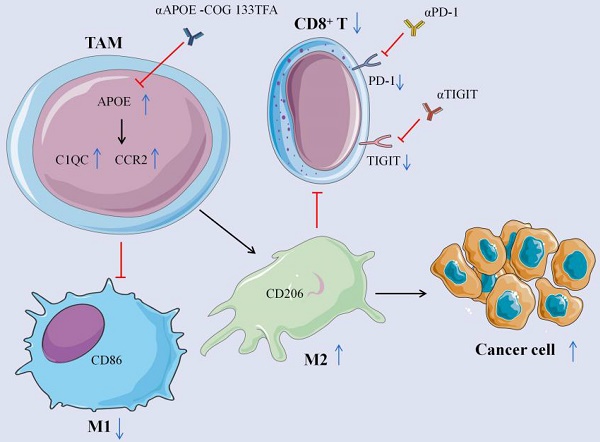
Checkpoint immunotherapy is capable of unleashing T cells for controlling tumor, whereas it is destroyed by immunosuppressive myeloid cell. Apoprotein E (APOE) refers to a ligand in terms of the members of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor family for mediating Apoprotein B-involving atherogenic lipoprotein clearance. Besides, tumor-infiltration macrophage can express APOE. The present study reported Apoe-/- mice to exhibit higher resistance toward the development of three types of carcinomas as compared with mice with wild type and to have greater responses to αPD-1 (anti-PD-1) immunotherapy. Moreover, treatment by exploiting APOE inhibitor (COG 133TFA, αAPOE) was capable of curbing tumor development and fostering regression if in combination of αPD-1. According to single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), Apoe deletion was correlated with the decline of C1QC+ and CCR2+ macrophage within tumor infiltration, and mass spectrometry results noticeably showed down-regulated the number of M2 macrophages as well. Furthermore, APOE expression in cancer patients resistant to αPD-1 treatment significantly exceeded that in the sensitive group. For this reason, APOE is likely to be targeted for modifying tumor macrophage infiltrate and augmenting checkpoint immunotherapy.
Keywords: single-cell RNA sequencing, APOE, PD-1, TIGIT, macrophage

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact