10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(14):5489-5502. doi:10.7150/ijbs.72977 This issue Cite
Research Paper
AANG Prevents Smad3-dependent Diabetic Nephropathy by Restoring Pancreatic β-Cell Development in db/db Mice
1. Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, The Chinese University of Hong Kong
2. Department of Anatomical and Cellular Pathology, State Key Laboratory of Translational Oncology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong
3. Research Center for Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, and Department of Cardiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
4. Guangdong-Hong Kong Joint Laboratory on Immunological and Genetic Kidney Diseases, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, Guangzhou, China
* Authors are equally contributed to this work.
Abstract
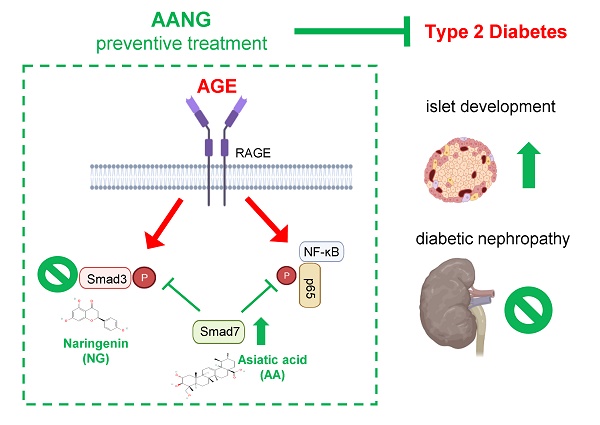
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a major cause of end-stage kidney disease, where TGF-β1/Smad signaling plays an important role in the disease progression. Our previous studies demonstrated a combination of Traditional Chinese Medicine derived Smad7 agonist Asiatic Acid (AA) and Smad3 inhibitor Naringenin (NG), AANG, effectively suppressed the progression of renal fibrosis in vivo. However, its implication in type-2 diabetic nephropathy (T2DN) is still unexplored. Here, we detected progressive activation of Smad3 but reduction of Smad7 in db/db mice during T2DN development. Therefore, we optimized the dosage and the combination ratio of AANG to achieve a better rebalancing Smad3/Smad7 signaling for treatment of T2DN. Unexpectedly, preventive treatment with combined AANG from week 4 before the development of diabetes and T2DN effectively protected against the onset of T2DN. In contract, these inhibitory effects were lost when db/db mice received the late AANG treatment from 12-24 weeks. Surprisingly, preventive treatment with AANG ameliorated not only T2DN but also the primary disease type-2 diabetes (T2D) with relative normal levels of fasting blood glucose and HbA1c, and largely improving metabolic abnormalities especially on insulin insensitivity and glucose tolerance in db/db mice. Mechanistically, AANG effectively prevented both Smad3-mediated renal fibrosis and NF-κB-driven renal inflammation in the diabetic kidney in vivo and advanced glycation end-products (AGE) stimulated tubular epithelial mTEC cells in vitro. More importantly, we uncovered that preventive treatment with AANG effectively protected against diabetic-associated islet injury via restoring the β cell development in db/db mice. Taken together, we discovered that the early treatment with combined AANG can effectively protect against the development of T2D and T2DN via mechanism associated with protection against Smad3-depenedent islet injury.
Keywords: Type-2 diabetes, Asiatic Acid, Naringenin, Islet, Nephropathy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact