10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(15):5653-5666. doi:10.7150/ijbs.73264 This issue Cite
Research Paper
TMP195 Exerts Antitumor Effects on Colorectal Cancer by Promoting M1 Macrophages Polarization
1. Department of Medical Oncology, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, College of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China.
2. The First Affiliated Hospital, and College of Clinical Medicine of Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471003, China.
* Equal contributors
Abstract
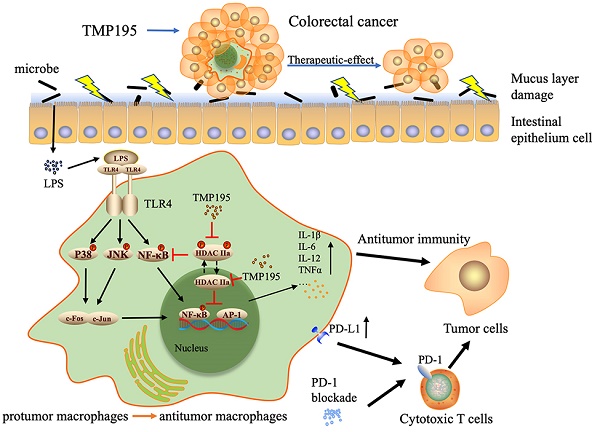
Studies have shown that epigenetic enzymes such as histone deacetylase (HDAC) are closely related to cancers and that several HDAC inhibitors exert antitumor effects. Studies have further suggested that class IIa HDAC inhibitors are related to immune functions, including immune responses and the expression of chemokines and complement pathway components. TMP195, a selective class IIa HDAC inhibitor, has been reported to be effective against breast cancer. However, the role and mechanism of TMP195 in colorectal cancer remain unknown. In this study, we found that TMP195 significantly reduced the tumor burden in two mouse models of colitis-associated colorectal cancer (CAC) and subcutaneous tumor. Mechanistically, TMP195 decreased the proportion of total macrophages but increased the proportion of M1 macrophages by promoting polarization, resulting in the increased release of inflammatory cytokines. TMP195 had no direct effect on the proliferation of colorectal cancer cells, and its antitumor effect on the colorectal cancer disappeared when macrophages were partly depleted by clodronate liposomes. In addition, TMP195 enhanced the efficacy of PD-1 blockade. The present study revealed that the combination of TMP195 and PD-1 blockade may provide a therapeutic strategy for colorectal cancer.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer, TMP195, HDAC, macrophage, PD-1 blockade

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact