10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2022; 18(15):5913-5927. doi:10.7150/ijbs.76936 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Integrated pathological analysis to develop a Gal-9 based immune survival stratification to predict the outcome of lung large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and its usefulness in immunotherapy
1. Department of Thoracic Surgery, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, China.
2. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, China.
3. Pathology Department, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China.
4. Department of Radiation Oncology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (CAMS) and Peking Union Medical College (PUMC), Beijing, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
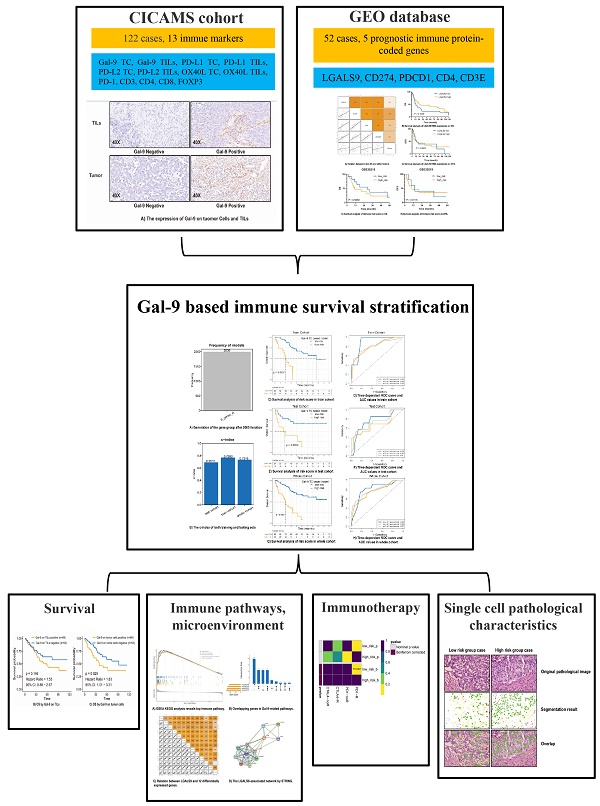
This study aimed to integrate the cell spatial organization to develop a Gal-9-based immune survival stratification in the lung large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) and investigate its potentials to immunotherapy.
The expression of Gal-9 and other twelve immune markers were evaluated in 122 cases of surgical LCNEC samples from our center using immunohistochemistry. The Gal-9-based immune survival stratification risk score was constructed and its predictive performance was evaluated. Then, we thoroughly explored the effects of Gal-9 and immune risk score on LCNEC immune pathways, immune micro-environment and immunotherapy sensitivity in different cohort and platform, and made a validation in pathology images using Histology-based Digital-Staining (HDS).
In 122 LCNEC samples, 43 cases were positive Gal-9 expression on tumor cells (Gal-9 TC). Increased Gal-9 TC predicted worse overall survival. Gal-9's interaction with other immune markers added to the immune suppression and immune tolerance in LCNEC. Immune protein marker-based risk score consisting of Gal-9, CD3, CD4, PD-L1, and PD-1 was developed and validated to robustly discriminate survival high-risk or low-risk in LCNEC patients. The high-risk group characterized by immune-desert tumor had less various T cells. The low-risk group featuring immune-inflamed tumor was more likely to respond to anti-PD1 immunotherapy. HDS in 122 LCNEC samples' 108,369 cells validated that the high-risk group had more tumor cells, less stromal cells, less lymphocytes, higher tumor cell nucleic solidity and lower stromal cells nucleic solidity.
An integrated pathological analysis confirms the Gal-9 based immune survival stratification is distinctively related to micro-environment status involved in immune suppression and immune tolerance and could act as a combinatorial biomarker to predict the outcome of LCNEC. These findings may help effectively stratify LCNEC patients sensitive to immunotherapy.
Keywords: large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, galectin-9, prognosis, biomarker, immunotherapy, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, immune suppression

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact