ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(2):377-392. doi:10.7150/ijbs.75852 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Neddylation of HER2 Inhibits its Protein Degradation and promotes Breast Cancer Progression
1. Affiliated Cancer Hospital & Institute of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510095, China.
2. Guangzhou Municipal and Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Protein Modification and Degradation, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 511436, China.
3. Department of Surgery, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas 75390, USA.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
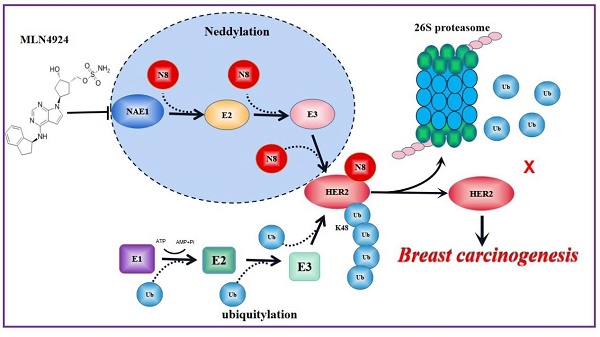
HER2 is a transmembrane receptor with intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity that is overexpressed in almost 25% of human breast cancers. Here, we report that the neddylation of HER2 is a new post-translational modification that controls its expression and oncogenic activity in human breast cancer. Two critical members in the neddylation pathway, NEDD8 and NEDD8-activating enzyme E1 subunit 1 (NAE1), are detected in human breast specimens. Overexpressed NEDD8 and NAE1 are positively correlated with HER2 expression in human breast cancer. Subsequent structure and function experiments show that HER2 directly interacts with NEDD8 and NAE1, whereas HER2 protein expression is decreased by neddylation depletion. Mechanistically, neddylation inhibition promotes the degradation of HER2 protein by improving its ubiquitination. HER2 overexpression abrogates neddylation depletion-triggered cell growth suppression. The inhibition of neddylation synergized with trastuzumab significantly suppresses growth of HER2 positive breast cancer. Collectively, this study demonstrates a previously undiscovered role of NEDD8-dependent HER2 neddylation promotes tumor growth in breast cancer.
Keywords: HER2, neddylation, ubiquitin, degradation, breast cancer

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact