10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(2):658-674. doi:10.7150/ijbs.77994 This issue Cite
Review
Targeting Necroptosis: A Novel Therapeutic Option for Retinal Degenerative Diseases
1. Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Central South University, Changsha, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Emergency and Trauma, Ministry of Education, College of Emergency and Trauma, Hainan Medical University, Haikou, China.
3. Changsha Aier Eye Hospital, Changsha, China.
4. School of Physical Education, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, China.
5. Affiliated Eye Hospital of Nanchang University, Jiangxi Research Institute of Ophthalmology and Visual Science, Jiangxi Clinical Research Center for Ophthalmic Disease, Nanchang, China.
6. Department of Ophthalmology, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China.
7. Beijing Tongren Eye Center, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
8. Beijing Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences Key Laboratory, Beijing, China.
9. Hunan Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Changsha, China.
Abstract
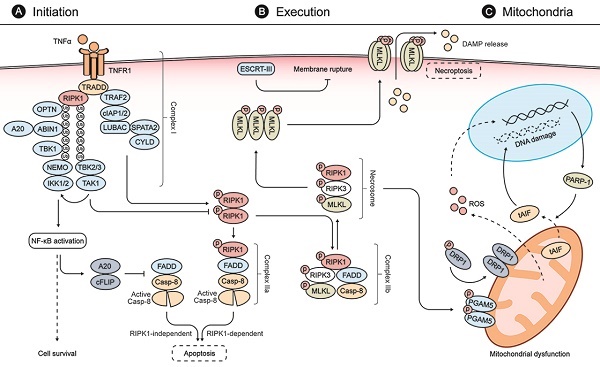
The discovery of the necroptosis, a form of regulated necrosis that is mediated by receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1), RIPK3, and mixed-lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase (MLKL), represents a major breakthrough that has dramatically altered the conception of necrosis - traditionally thought of as uncontrolled cell death - in various human diseases. Retinal cell death is a leading cause of blindness and has been identified in most retinal diseases, e.g., age-related macular degeneration, glaucoma, retinal detachment, retinitis pigmentosa, etc. Increasing evidence demonstrates that retinal degenerative diseases also share a common mechanism in necroptosis. Exacerbated necroptotic cell death hinders the treatment for retinal degenerative diseases. In this review, we highlight recent advances in identifying retinal necroptosis, summarize the underlying mechanisms of necroptosis in retinal degenerative diseases, and discuss potential anti-necroptosis strategies, such as selective inhibitors and chemical agents, for treating retinal degenerative diseases.
Keywords: Retinal degenerative diseases, necroptosis, RIPK1, RIPK3, age-related macular degeneration, glaucoma

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact