10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(4):1094-1109. doi:10.7150/ijbs.79666 This issue Cite
Review
Extracellular Vesicles in Mental Disorders: A State-of-art Review
1. Department of Psychiatry, the First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310003, China.
2. The Key Laboratory of Mental Disorder's Management in Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou 310003, China.
3. Brain Research Institute of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310003, China.
4. Zhejiang Engineering Center for Mathematical Mental Health, Hangzhou 310003, China.
5. Department of Neurobiology, NHC and CAMS Key Laboratory of Medical Neurobiology, School of Brain Science and Brian Medicine, and MOE Frontier Science Center for Brain Science and Brain-machine Integration, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310003, China.
6. Peking University Sixth Hospital, Peking University Institute of Mental Health, NHC Key Laboratory of Mental Health (Peking University), National Clinical Research Center for Mental Disorders (Peking University Sixth Hospital), Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Research Unit (No.2018RU006), Peking University, Beijing, China.
7. Peking-Tsinghua Center for Life Sciences and PKU-IDG/McGovern Institute for Brain Research, Peking University, Beijing, China.
8. Department of Pathology, First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Zhejiang, China.
9. National Health and Disease Human Brain Tissue Resource Center, Zhejiang University, Zhejiang, China.
*These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
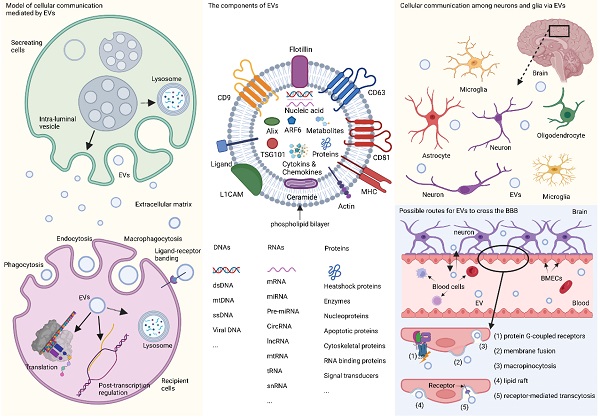
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanoscale particles with various physiological functions including mediating cellular communication in the central nervous system (CNS), which indicates a linkage between these particles and mental disorders such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, etc. To date, known characteristics of mental disorders are mainly neuroinflammation and dysfunctions of homeostasis in the CNS, and EVs are proven to be able to regulate these pathological processes. In addition, studies have found that some cargo of EVs, especially miRNAs, were significantly up- or down-regulated in patients with mental disorders. For many years, interest has been generated in exploring new diagnostic and therapeutic methods for mental disorders, but scale assessment and routine drug intervention are still the first-line applications so far. Therefore, underlying the downstream functions of EVs and their cargo may help uncover the pathogenetic mechanisms of mental disorders as well as provide novel biomarkers and therapeutic candidates. This review aims to address the connection between EVs and mental disorders, and discuss the current strategies that focus on EVs-related psychiatric detection and therapy.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicle, non-coding RNA, mental disorder, biomarker

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact