ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(4):1110-1122. doi:10.7150/ijbs.82015 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Phosphorylation by IKKβ Promotes the Degradation of HMGCL via NEDD4 in Lung Cancer
1. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Shanghai Chest Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 200030, Shanghai, China.
2. Department of Thoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, 650032, Yunnan, China.
3. Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. The First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, 650032, Yunnan, China.
4. Shanghai Institute of Thoracic Oncology, Shanghai Chest Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 200030, Shanghai, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
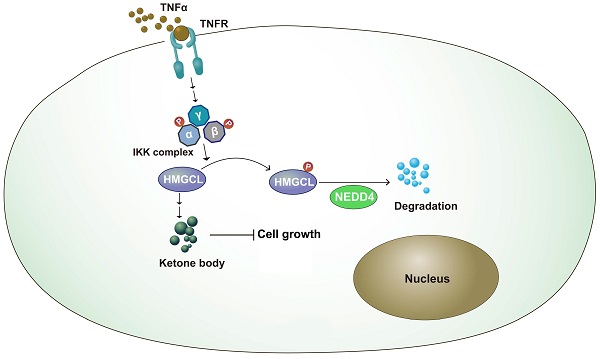
Inflammation and metabolic reprogramming are hallmarks of cancer. How inflammation regulates cancer metabolism remains poorly understood. In this study, we found that 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase (HMGCL), the enzyme that catalyzes the catabolism of leucine and promotes the synthesis of ketone bodies, was downregulated in lung cancer. Downregulation of HMGCL was associated with a larger tumor size and a shorter overall survival time. In a functional study, overexpression of HMGCL increased the content of β-hydroxybutyrate (β-HB) and inhibited the tumorigenicity of lung cancer cells, and deletion of HMGCL promoted de novo tumorigenesis in KP (KrasG12D;P53f/f) mice. Mechanistically, tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) treatment decreased the HMGCL protein level, and IKKβ interacted with HMGCL and phosphorylated it at Ser258, which destabilized HMGCL. Moreover, NEDD4 was identified as the E3 ligase for HMGCL and promoted its degradation. In addition, mutation of Ser258 to alanine inhibited the ubiquitination of HMGCL by NEDD4 and thus inhibited the anchorage-independent growth of lung cancer cells more efficiently than did wild-type HMGCL. In summary, this study demonstrated a link between TNFα-mediated inflammation and cancer metabolism.
Keywords: Lung cancer, Ketone body, HMGCL, IKKβ, NEDD4

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact