10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(4):1192-1210. doi:10.7150/ijbs.80775 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Mitophagy alleviates cisplatin-induced renal tubular epithelial cell ferroptosis through ROS/HO-1/GPX4 axis
1. Department of Nephrology, Molecular Cell Lab for Kidney Disease, Shanghai Peritoneal Dialysis Research Center, Ren Ji Hospital, Uremia Diagnosis and Treatment Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200127, China
2. Department of Nephrology, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201200, China
3. Tianping Community Health Service Center, Shanghai, 200031, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
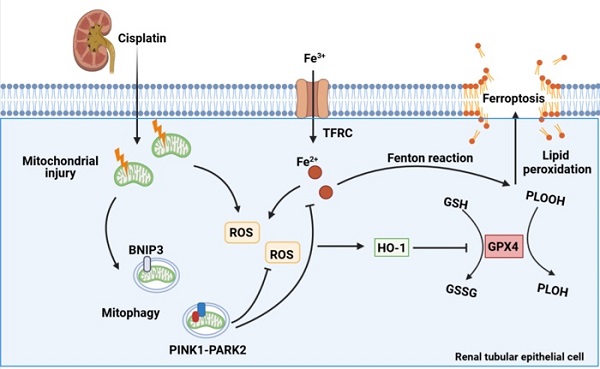
Cisplatin is widely recommended in combination for the treatment of tumors, thus inevitably increasing the incidence of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Mitophagy is a type of mitochondrial quality control mechanism that degrades damaged mitochondria and maintains cellular homeostasis. Ferroptosis, a new modality of programmed cell death, is characterized by iron-dependent phospholipid peroxidation and oxidative membrane damage. However, the role of mitophagy in ferroptosis in kidney disease is unclear. Here, we investigated the mechanism underlying both BNIP3-mediated and PINK1-PARK2-mediated mitophagy-induced attenuation of ferroptosis in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. The results showed that cisplatin induced mitochondrial injury, ROS release, intracellular iron accumulation, lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in the kidney, which were aggravated in Bnip3 knockout, Pink1 knockout or Park2 knockout cisplatin-treated mice. Ferrstatin-1, a synthetic antioxidative ferroptosis inhibitor, rescued iron accumulation, lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis caused by inhibition of mitophagy. Thus, the present study elucidated a novel mechanism by which both BNIP3-mediated and PINK1-PARK2-mediated mitophagy protects against cisplatin-induced renal tubular epithelial cell ferroptosis through the ROS/HO1/GPX4 axis.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury, cisplatin nephrotoxicity, ferroptosis, mitophagy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact