Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(5):1413-1429. doi:10.7150/ijbs.79913 This issue Cite
Research Paper
PD-L1 promotes GSDMD-mediated NET release by maintaining the transcriptional activity of Stat3 in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
1. Faculty of Anesthesiology, Changhai Hospital, Naval Medical University, Shanghai, People's Republic of China
2. Jiangsu Province Key Laboratory of Anesthesiology, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, Jiangsu Province, People's Republic of China
3. Faculty of Anesthesiology, Weifang Medical University, Weifang, Shandong Province, People's Republic of China
†These authors have contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
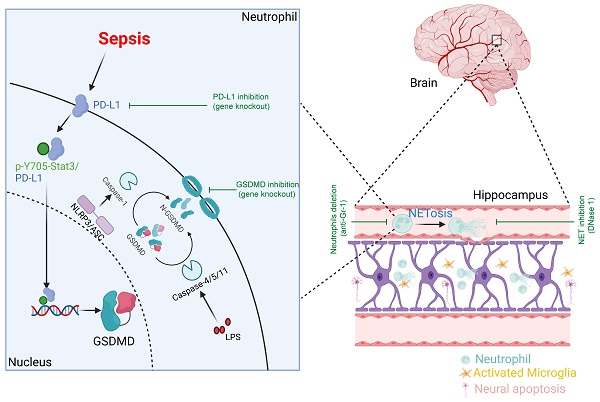
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE), as shown as acute and long-term cognitive impairment, is associated with increased mortality of sepsis. The causative factors of SAE are diverse and the underlying pathological mechanisms of SAE remain to be fully elucidated. Multiple studies have demonstrated a crucial role of microglia in the development of SAE, but the role of neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in SAE is still unclear. Here, we firstly show that in murine sepsis model, neutrophils and NETs promote blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption, neuronal apoptosis and microglia activation in hippocampus and induce hippocampus-dependent memory impairment. Anti-Gr-1 antibody or DNase I treatment attenuates these sepsis-induced changes. Then, we find that genetic deletion of neutrophil GSDMD or PD-L1 reduces NET release and improves SAE in murine sepsis model. Finally, in human septic neutrophils, p-Y705-Stat3 binds to PD-L1, promotes PD-L1 nuclear translocation and enhances transcription of the gasdermin D (GSDMD) gene. In summary, our findings firstly identify a novel function of PD-L1 in maintaining transcriptional activity of p-Y705-Stat3 to promote GSDMD-dependent NET release in septic neutrophils, which plays a critical role in the development of SAE.
Keywords: sepsis-associated encephalopathy, neutrophil, neutrophil extracellular traps, PD-L1, gasdermin D

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact