Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(5):1616-1632. doi:10.7150/ijbs.79467 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells via METTL3-mediated RAC3 m6A modification
1. Tianjin Key Laboratory of Lung Cancer Metastasis and Tumor Microenvironment, Tianjin Lung Cancer Institute, Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin 300052, China.
2. Department of Clinical Laboratory, Shandong Cancer Hospital and Institute, Shandong First Medical University and Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan 250117, China.
3. Department of Anesthesiology, Tianjin First Central Hospital, Tianjin 300192, China.
4. Core Facility Center, Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin 300052, China.
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
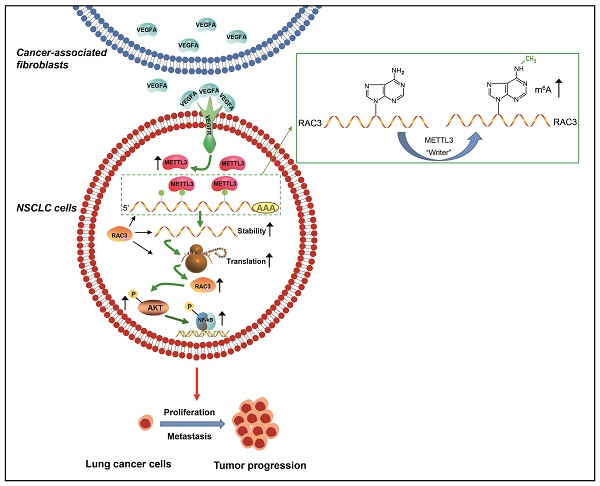
Cancer progression depends on the communication between tumor cells and tumor microenvironment. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are a major component of stromal cells. CAFs promote cancer metastasis; however, it has not been evaluated whether N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification is responsible for CAFs' role in metastasis. In the present study, we found that CAFs promoted migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells by elevating m6A modification in NSCLC cells. Methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3) in NSCLC cells mediated CAFs' effect on m6A modification, and was regulated by CAFs-secreted vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA). METTL3 knockdown in NSCLC cells dramatically inhibited cell migration and invasion, and suppressed tumor growth in vivo. Database analysis revealed that METTL3 was associated with poor prognosis of lung cancer. The mechanism study showed that METTL3 increased m6A level of RAC3 mRNA, resulting in increased stability and translation of RAC3 mRNA. RAC3 was responsible for the CAFs' promoting effect on cell migration via the AKT/NF-κB pathway. This study established a CAF-METTL3-RAC3 m6A modification-dependent regulation system in NSCLC metastasis, suggesting potential candidates for metastasis treatment.
Keywords: Lung cancer, Metastasis, Cancer-associated fibroblasts, m6A, METTL3, RAC3

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact