10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(9):2803-2816. doi:10.7150/ijbs.81726 This issue Cite
Research Paper
TRIM26 promotes non-small cell lung cancer survival by inducing PBX1 degradation
1. Guangdong Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, Guangdong Key Laboratory of Vascular Diseases, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, 511436, P. R. China.
2. Guangdong Key Laboratory of Protein Modification and Degradation, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, 511436, P. R. China.
3. Department of Pharmacology, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu, 215123, P. R. China.
4. Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, P. R. China.
5. Department of Biology, GMU-GIBH Joint School of Life Sciences, The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Joint Laboratory for Cell Fate Regulation, Guangzhou Medical University, 511436, P. R. China.
6. Division of Hematology & Oncology, Department of Geriatrics, Guangzhou First People's Hospital, College of Medicine, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510180, P. R. China.
7. Department of Urology, Jinling Hospital of Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210093, P. R. China
# These authors contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
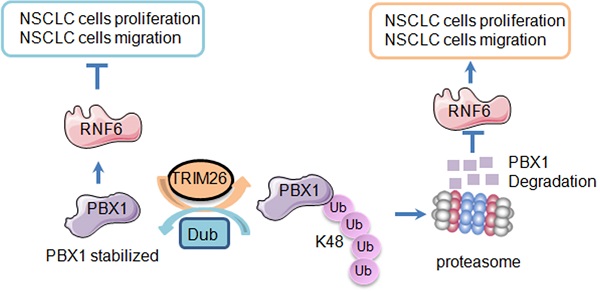
The transcription factor PBX1 is regarded as an oncogene in various cancers, but its role in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and the detailed mechanism is not known. In the present study, we found that PBX1 is downregulated in NSCLC tissues and inhibits NSCLC cell proliferation and migration. Subsequently, we performed an affinity purification-coupled tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) and found the ubiquitin ligase TRIM26 in the PBX1 immunoprecipitates. Moreover, TRIM26 binds to and mediates PBX1 for K48-linked polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Noticeably, TRIM26 activity depends on its C-terminal RING domain when it is deleted TRIM26 loses its function towards PBX1. TRIM26 further inhibits PBX1 transcriptional activity and downregulates the PBX1 downstream genes, such as RNF6. Moreover, we found that overexpression of TRIM26 significantly promotes NSCLC proliferation, colony formation, and migration in contradiction to PBX1. TRIM26 is highly expressed in NSCLC tissues and predicts poor prognosis. Lastly, the growth NSCLC xenografts is promoted by overexpression of TRIM26 but is suppressed by TRIM26 knockout. In conclusion, TRIM26 is a ubiquitin ligase of PBX1 and it promotes while PBX1 inhibits NSCLC tumor growth. TRIM26 might be a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer, Pre-B cell leukemia transcription factor 1, Tripartite motif containing 26

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact