10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(10):3077-3098. doi:10.7150/ijbs.83392 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Inhibition of KMO Ameliorates Myocardial Ischemia Injury via Maintaining Mitochondrial Fusion and Fission Balance
1. Jiangsu Key Laboratory of TCM Evaluation and Translational Research, Research Center for Traceability and Standardization of TCMs, School of Traditional Chinese Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, 639 Longmian Road, Nanjing, 211198, China.
2. Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, 210029, China.
#These authors contributed equally: Qiong Lai, Lingling Wu
Abstract
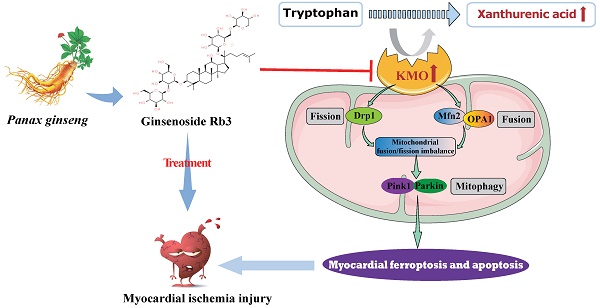
Looking for early diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets is the key to ensuring prompt treatment of myocardial ischemia (MI). Here, a novel biomarker xanthurenic acid (XA) was identified based on metabolomics and exhibited high sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of MI patients. Additionally, the elevation of XA was proved to induce myocardial injury in vivo by promoting myocardial apoptosis and ferroptosis. Combining metabolomics and transcriptional data further revealed that kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO) profoundly increased in MI mice, and was closely associated with the elevation of XA. More importantly, pharmacological or heart-specific inhibition of KMO obviously suppressed the elevation of XA and profoundly ameliorated the OGD-induced cardiomyocytes injury and the ligation-induced MI injury. Mechanistically, KMO inhibition effectively restrained myocardial apoptosis and ferroptosis by modulating mitochondrial fission and fusion. In addition, virtual screening and experimental validation were adopted to identify ginsenoside Rb3 as a novel inhibitor of KMO and exhibited great cardioprotective effects by regulating mitochondrial dynamical balance. Taken together, targeting KMO may provide a new approach for the clinical treatment of MI through maintaining mitochondrial fusion and fission balance, and ginsenoside Rb3 showed great potential to be developed as a novel therapeutic drug targeting KMO.
Keywords: Myocardial ischemia, Xanthurenic acid, Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase, Mitochondrial fusion and fission, Ginsenoside Rb3

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact