10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(11):3341-3359. doi:10.7150/ijbs.82317 This issue Cite
Review
CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 Axis in Cancer: from Mechanisms to Clinical Applications
1. Department of Orthopedics, Shenmu Hospital, Faculty of Life Sciences and Medicine, Northwest University, Shenmu, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Resource Biology and Biotechnology in Western China, Ministry of Education. Faculty of Life Sciences and Medicine, Northwest University, Xi'an, China.
3. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Tangdu Hospital, The Airforce Medical University, Xi'an, China.
4. Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Central Theater Command General Hospital of Chinese People's Liberation Army, Wuhan, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
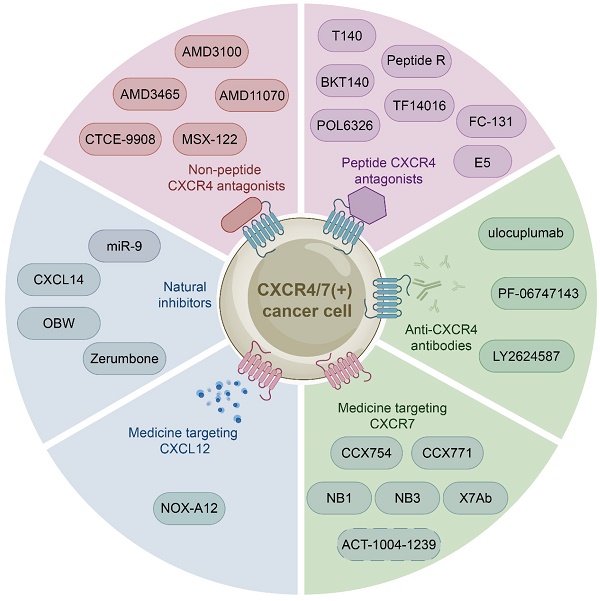
Cancer is a multi-step disease caused by the accumulation of genetic mutations and/or epigenetic changes, and is the biggest challenge around the world. Cytokines, including chemokines, exhibit expression changes and disorders in all human cancers. These cytokine abnormalities can disrupt homeostasis and immune function, and make outstanding contributions to various stages of cancer development such as invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis. Chemokines are a superfamily of small molecule chemoattractive cytokines that mediate a variety of cellular functions. Importantly, the interactions of chemokine members CXCL12 and its receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 have a broad impact on tumor cell proliferation, survival, angiogenesis, metastasis, and tumor microenvironment, and thus participate in the onset and development of many cancers including leukemia, breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer and multiple myeloma. Therefore, this review aims to summarize the latest research progress and future challenges regarding the role of CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 signaling axis in cancer, and highlights the potential of CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 as a biomarker or therapeutic target for cancer, providing essential strategies for the development of novel targeted cancer therapies.
Keywords: Chemokine CXCL12, CXCR4, CXCR7, Cancer progression, Inhibitors

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact