10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(11):3383-3394. doi:10.7150/ijbs.82556 This issue Cite
Review
Interplay Between the Immune and Nervous Cognitive Systems in Homeostasis and in Malaria
1. Laboratório de Pesquisa em Malária, Instituto Oswaldo Cruz & Centro de Pesquisa, Diagnóstico e Treinamento em Malária (CPD-Mal) from Fundação Oswaldo Cruz (Fiocruz) and the Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde (SVS), Ministério da Saúde, Brazil.
2. Laboratório de Biologia, campus Duque de Caxias, Colégio Pedro II, Brazil.
Abstract
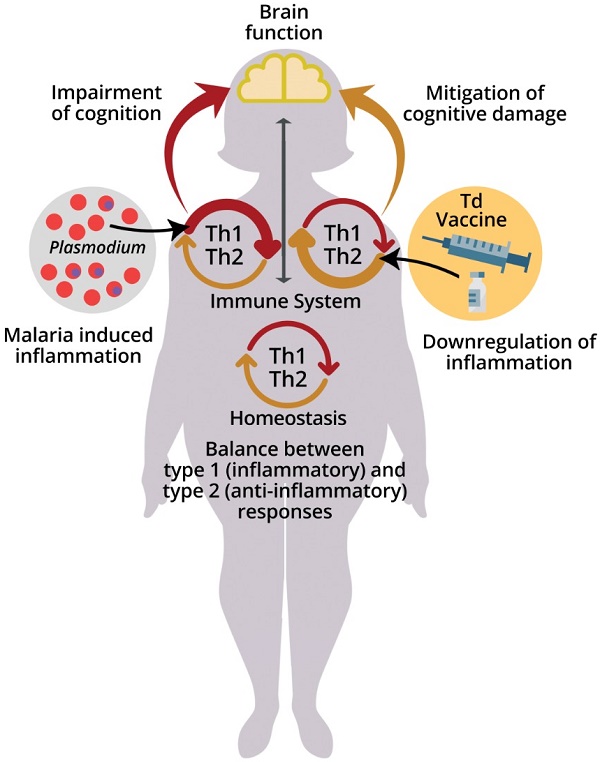
The immune and nervous systems can be thought of as cognitive and plastic systems, since they are both involved in cognition/recognition processes and can be architecturally and functionally modified by experience, and such changes can influence each other's functioning. The immune system can affect nervous system function depending on the nature of the immune stimuli and the pro/anti-inflammatory responses they generate. Here we consider interactions between the immune and nervous systems in homeostasis and disease, including the beneficial and deleterious effects of immune stimuli on brain function and the impact of severe and non-severe malaria parasite infections on neurocognitive and behavioral parameters in human and experimental murine malaria. We also discuss the effect of immunization on the reversal of cognitive deficits associated with experimental non-severe malaria in a model susceptible to the development of the cerebral form of the illness. Finally, we consider the possibility of using human vaccines, largely exploited as immune-prophylactics for infectious diseases, as therapeutic tools to prevent or mitigate the expression of cognitive deficits in infectious and chronic degenerative diseases.
Keywords: immune system, nervous system, homeostasis, malaria, neurocognitive impairment.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact