10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2023; 19(16):5036-5054. doi:10.7150/ijbs.85590 This issue Cite
Review
Potential Roles of Metals in the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary and Systemic Hypertension
1. Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, KY, USA.
2. Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Pulmonary Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE, USA.
3. Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, Department of Medicine, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, KY, USA.
4. The Center for Integrative Environmental Health Sciences, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY, 40202, USA.
5. Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, KY, USA.
6. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, KY, USA.
7. The Transplant Program at UofL Health - Jewish Hospital Trager Transplant Center, Louisville, KY, USA.
8. Pediatric Research Institute, Department of Pediatrics, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, KY, USA.
9. Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, KY, USA.
10. Cardiovascular Innovation Institute, Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, KY, USA.
Abstract
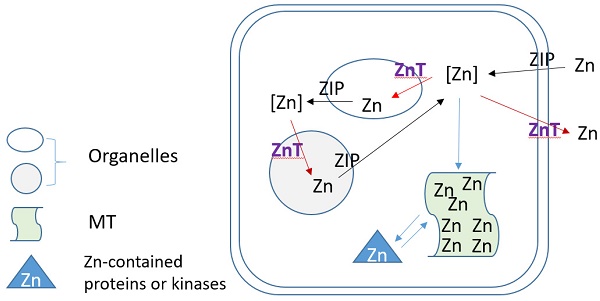
Pulmonary and systemic hypertension (PH, SH) are characterized by vasoconstriction and vascular remodeling resulting in increased vascular resistance and pulmonary/aortic artery pressures. The chronic stress leads to inflammation, oxidative stress, and infiltration by immune cells. Roles of metals in these diseases, particularly PH are largely unknown. This review first discusses the pathophysiology of PH including vascular oxidative stress, inflammation, and remodeling in PH; mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic changes in PH; ion channel and its alterations in the pathogenesis of PH as well as PH-associated right ventricular (RV) remodeling and dysfunctions. This review then summarizes metal general features and essentiality for the cardiovascular system and effects of metals on systemic blood pressure. Lastly, this review explores non-essential and essential metals and potential roles of their dyshomeostasis in PH and RV dysfunction. Although it remains early to conclude the role of metals in the pathogenesis of PH, emerging direct and indirect evidence implicates the possible contributions of metal-mediated toxicities in the development of PH. Future research should focus on comprehensive clinical metallomics study in PH patients; mechanistic evaluations to elucidate roles of various metals in PH animal models; and novel therapy clinical trials targeting metals. These important discoveries will significantly advance our understandings of this rare yet fatal disease, PH.
Keywords: Pulmonary artery hypertension, Pulmonary hypoxia, Right ventricle dysfunction, Trace elements, Mineral homeostasis, Heavy metals, Non-essential metals, Mitochondrial dysfunction, Hypertension

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact