Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(1):127-136. doi:10.7150/ijbs.89890 This issue Cite
Review
The role of TNC in atherosclerosis and drug development opportunities
1. Cancer Institute, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao University, Qingdao Cancer Institute, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071, China.
2. Department of Pharmacy, Women's and Children's Hospital Afliated to Qingdao University, Qingdao Women's and Children's Hospital, Qingdao, Shandong, 266000, China.
3. Obstetrical Department, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, Shandong, 266003, China
4. Qingdao Medical College, Qingdao University, Qingdao, Shandong, 266071, China.
5. School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
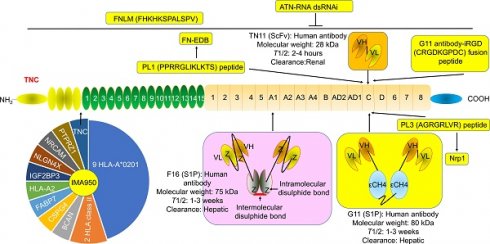
Tenascin C (TNC), a rich glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix, exhibits a pro-atherosclerosis or anti-atherosclerosis effect depending on its location. TNC, especially its C domain/isoform (TNC-C), is strongly overexpressed in atherosclerotic plaque active areas but virtually undetectable in most normal adult tissues, suggesting that TNC is a promising delivery vector target for atherosclerosis-targeted drugs. Many delivery vectors were investigated by recognizing TNC-C, including G11, G11-iRGD, TN11, PL1, and PL3. F16 and FNLM were also investigated by recognizing TNC-A1 and TNC, respectively. Notably, iRGD was undergoing clinical trials. PL1 not only recognizes TNC-C but also the extra domain-B (EDB) of fibronectin (FN), which is also a promising delivery vector for atherosclerosis-targeted drugs, and several conjugate agents are undergoing clinical trials. The F16-conjugate agent F16IL2 is undergoing clinical trials. Therefore, G11-iRGD, PL1, and F16 have great development value. Furthermore, ATN-RNA and IMA950 were investigated in clinical trials as therapeutic drugs and vaccines by targeting TNC, respectively. Therefore, targeting TNC could greatly improve the success rate of atherosclerosis-targeted drugs and/or specific drug development. This review discussed the role of TNC in atherosclerosis, atherosclerosis-targeted drug delivery vectors, and agent development to provide knowledge for drug development targeting TNC.
Keywords: TNC, atherosclerosis, G11-iRGD, PL1, F16, ATN-RNA, drug development

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact