10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(1):175-181. doi:10.7150/ijbs.86305 This issue Cite
Review
Mechanisms underlying therapeutic resistance of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia
1. Hematology Department, First hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, 130021, P.R. China.
2. Stanford University Medical School, Palo Alto Veterans Institute for Research, Palo Alto, CA94304, USA.
3. Oncology Department, Cancer hospital Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Langfang District, 065001, P.R. China.
Abstract
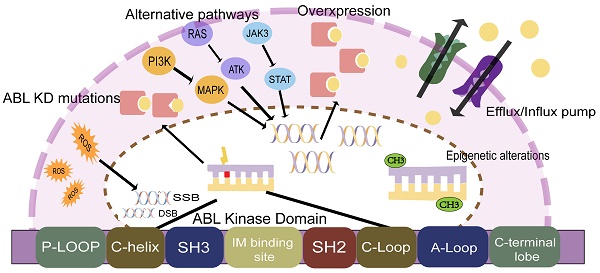
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a malignant clonal disease involving hematopoietic stem cells that is characterized by myeloid cell proliferation in bone marrow and peripheral blood, and the presence of the Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome with BCR-ABL fusion gene. Treatment of CML has dramatically improved since the advent of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI). However, there are a small subset of CML patients who develop resistance to TKI. Mutations in the ABL kinase domain (KD) are currently recognized as the leading cause of TKI resistance in CML. In this review, we discuss the concept of resistance and summarize recent advances exploring the mechanisms underlying CML resistance. Overcoming TKI resistance appears to be the most successful approach to reduce the burden of leukemia and enhance cures for CML. Advances in new strategies to combat drug resistance may rapidly change the management of TKI-resistant CML and expand the prospects for available therapies.
Keywords: chronic myeloid leukemia, TKI Resistance, ABL mutation, mechanism

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact