10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(1):200-217. doi:10.7150/ijbs.87820 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Treatment for type 2 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy by targeting Smad3 signaling
1. Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, Guangdong, 519000, China; Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Biomedical Imaging, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province, 519000, China
2. Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, and Li Ka Shing Institute of Health Sciences, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong; and Guangdong-Hong Kong Joint Laboratory on Immunological and Genetic Kidney Diseases, and Departments of Nephrology and Pathology, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510080, China.
Abstract
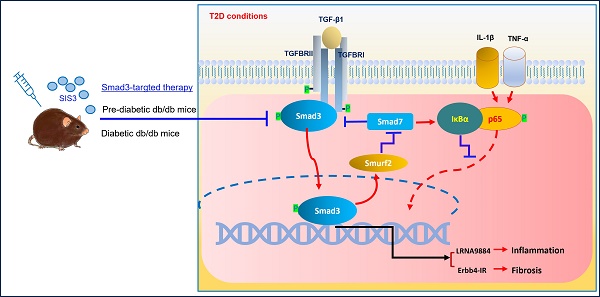
TGF-β/Smad3 signaling plays a critical role in type 2 diabetes (T2D) and type 2 diabetic nephropathy (T2DN), but treatment by specifically targeting Smad3 remains unexplored. To develop a new Smad3-targeted therapy for T2D and T2DN, we treated db/db mice at the pre-diabetic or established diabetic stage with a pharmacological Smad3 inhibitor SIS3. The therapeutic effect and mechanisms of anti-Smad3 treatment on T2D and T2DN were investigated. We found that anti-Smad3 treatment on pre-diabetic db/db mice largely attenuated both T2D and T2DN by markedly reducing blood glucose levels, and inhibiting the elevated serum creatinine, microalbuminuria, and renal fibrosis and inflammation. Unexpectedly, although SIS3 treatment on the established diabetic db/db mice inhibited T2DN but did not significantly improve T2D. Mechanistically, we uncovered that inhibition of T2DN in SIS3-treated db/db mice was associated with effectively restoring the balance of TGF-β/Smad signaling by inhibiting Smad3 while increasing Smad7, thereby suppressing Smad3-mediated renal fibrosis and NF-κB-driven renal inflammation via lncRNA Erbb4-IR and LRN9884-dependent mechanisms. We also revealed that inhibition of islet β cell injury by preventing the loss of islet Pax 6 could be the mechanism through which the pre-diabetic treatment, rather than the late SIS3 treatment on db/db mice significantly improved the T2D phenotype.
Keywords: Type-2 diabetes, Smad3 inhibitor, Treatment, Islet, Nephropathy

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact