10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(3):864-879. doi:10.7150/ijbs.89795 This issue Cite
Review
Endometrial Stem Cells: Orchestrating Dynamic Regeneration of Endometrium and Their Implications in Diverse Endometrial Disorders
1. Department of Health Sciences and Technology, GAIHST, Gachon University, Incheon, 21999, Republic of Korea.
2. Department of Molecular Medicine, School of Medicine, Gachon University, Incheon 406-840, Republic of Korea.
Abstract
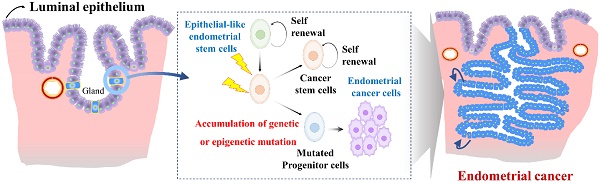
The human endometrium, a vital component of the uterus, undergoes dynamic changes during the menstrual cycle to create a receptive environment for embryo implantation. Its remarkable regenerative capacity can be attributed to the presence of tissue-resident stem cell populations within the endometrium. Despite variations in characteristics among different subtypes, endometrial stem cells exhibit notably robust self-renewal capacity and the ability to differentiate into multiple lineages. This review offers a comprehensive insight into the current literature and recent advancements regarding the roles of various endometrial stem cell types during dynamic regeneration of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle. In addition, emerging evidence suggests that dysfunction or depletion of endometrial stem cells may play critical roles in the development and progression of various endometrial disorders, such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, infertility, and endometrial cancer. Therefore, we also highlight potential roles of endometrial stem cells in the development and progression of these endometrial diseases, including their ability to accumulate genetic mutations and express genes associated with endometrial diseases. Understanding the dynamic properties of the endometrium and the roles of endometrial stem cells in various endometrial disorders will shed light on potential therapeutic strategies for managing these conditions and improving women's fertility outcomes.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact