10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(5):1634-1651. doi:10.7150/ijbs.92211 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Hypoxia-activated selectivity-improved anti-PKM2 antibody combined with prodrug TH-302 for potentiated targeting therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma
1. Department of Cell Biology, School of Medicine, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300071, China.
2. National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, Tianjin, 300060, China.
3. Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, St. John's University, Queens, New York, NY, 11439, USA.
† These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
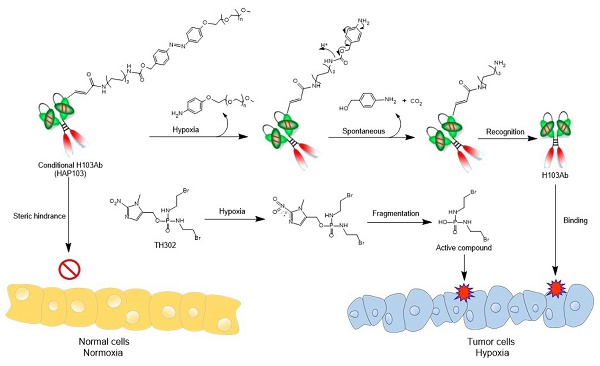
Background: Hypoxia induces hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) malignancies; yet it also offers treatment opportunities, exemplified by developing hypoxia-activated prodrugs (HAPs). Although HAP TH-302 combined with therapeutic antibody (Ab) has synergistic effects, the clinical benefits are limited by the on-target off-tumor toxicity of Ab. Here, we sought to develop a hypoxia-activated anti-M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase (PKM2) Ab combined with TH-302 for potentiated targeting therapy.
Methods: Codon-optimized and hypoxia-activation strategies were used to develop H103 Ab-azo-PEG5k (HAP103) Ab. Hypoxia-activated HAP103 Ab was characterized, and hypoxia-dependent antitumor and immune activities were evaluated. Selective imaging and targeting therapy with HAP103 Ab were assessed in HCC-xenografted mouse models. Targeting selectivity, systemic toxicity, and synergistic therapeutic efficacy of HAP103 Ab with TH-302 were evaluated.
Results: Human full-length H103 Ab was produced in a large-scale bioreactor. Azobenzene (azo)-linked PEG5k conjugation endowed HAP103 Ab with hypoxia-activated targeting features. Conditional HAP103 Ab effectively inhibited HCC cell growth, enhanced apoptosis, and induced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) functions. Analysis of HCC-xenografted mouse models showed that HAP103 Ab selectively targeted hypoxic HCC tissues and induced potent tumor-inhibitory activity either alone or in combination with TH-302. Besides the synergistic effects, HAP103 Ab had negligible side effects when compared to parent H103 Ab.
Conclusion: The hypoxia-activated anti-PKM2 Ab safely confers a strong inhibitory effect on HCC with improved selectivity. This provides a promising strategy to overcome the on-target off-tumor toxicity of Ab therapeutics; and highlights an advanced approach to precisely kill HCC in combination with HAP TH-302.
Keywords: Hypoxia-activated antibody, On-target off-tumor toxicity, TH-302, PKM2, Hepatocellular carcinoma

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact