10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(5):1884-1904. doi:10.7150/ijbs.92125 This issue Cite
Review
Reprogramming of Lipid Metabolism Mediates Crosstalk, Remodeling, and Intervention of Microenvironment Components in Breast Cancer
1. State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicines, Faculty of Chinese Medicine, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macau, China.
2. College of First Clinical Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China.
3. College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China.
4. College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shandong Second Medical University, Weifang, China.
5. Department of Oncology, Weifang Traditional Chinese Hospital, Weifang, China.
*Jia Wang and Wenfeng Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
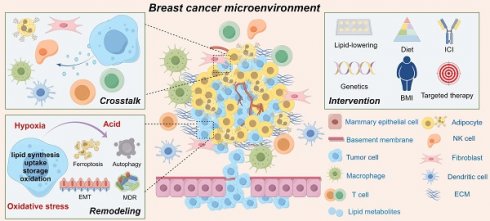
Due to the unique characteristics of breast cancer initiation sites and significant alterations in tumor metabolism, breast cancer cells rely on lipid metabolic reprogramming to effectively regulate metabolic programs during the disease progression cascade. This adaptation enables them to meet the energy demands required for proliferation, invasion, metastasis, and responses to signaling molecules in the breast cancer microenvironment. In this review, we comprehensively examined the distinctive features of lipid metabolic reprogramming in breast cancer and elucidated the underlying mechanisms driving aberrant behavior of tumor cells. Additionally, we emphasize the potential role and adaptive changes in lipid metabolism within the breast cancer microenvironment, while summarizing recent preclinical studies. Overall, precise control over lipid metabolism rewiring and understanding of plasticity within the breast cancer microenvironment hold promising implications for developing targeted treatment strategies against this disease. Therefore, interventions targeting the lipid metabolism in breast cancer may facilitate innovative advancements in clinical applications.
Keywords: Lipid metabolism, Breast cancer, Tumor microenvironment, Targeted intervention

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact