10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(6):2151-2167. doi:10.7150/ijbs.92525 This issue Cite
Review
Advancements in technology for characterizing the tumor immune microenvironment
Department of Pathology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei 430060, P.R. China.
Abstract
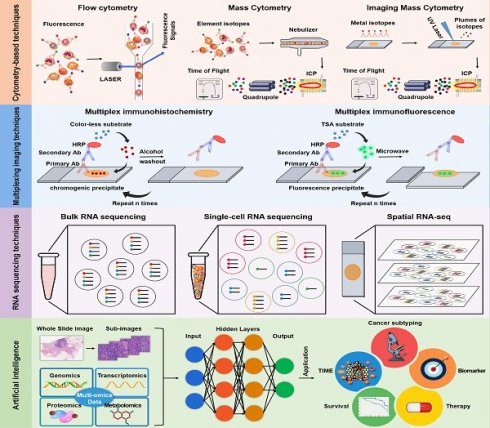
Immunotherapy plays a key role in cancer treatment, however, responses are limited to a small number of patients. The biological basis for the success of immunotherapy is the complex interaction between tumor cells and tumor immune microenvironment (TIME). Historically, research on tumor immune constitution was limited to the analysis of one or two markers, more novel technologies are needed to interpret the complex interactions between tumor cells and TIME. In recent years, major advances have already been made in depicting TIME at a considerably elevated degree of throughput, dimensionality and resolution, allowing dozens of markers to be labeled simultaneously, and analyzing the heterogeneity of tumour-immune infiltrates in detail at the single cell level, depicting the spatial landscape of the entire microenvironment, as well as applying artificial intelligence (AI) to interpret a large amount of complex data from TIME. In this review, we summarized emerging technologies that have made contributions to the field of TIME, and provided prospects for future research.
Keywords: Tumor immune microenvironment, Cytometry-based techniques, Multiplexing imaging techniques, RNA sequencing, Artificial intelligence

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact