10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(8):2943-2964. doi:10.7150/ijbs.91957 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Endothelial Dickkopf-1 Promotes Smooth Muscle Cell-derived Foam Cell Formation via USP53-mediated Deubiquitination of SR-A During Atherosclerosis
1. National Key Laboratory for Innovation and Transformation of Luobing Theory; The Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Remodeling and Function Research, Chinese Ministry of Education, Chinese National Health Commission and Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences; Department of Cardiology, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, China.
2. Department of Immunology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Shandong University, Jinan, China.
3. Department of Physiology & Pathophysiology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Shandong University, Jinan, China.
Abstract
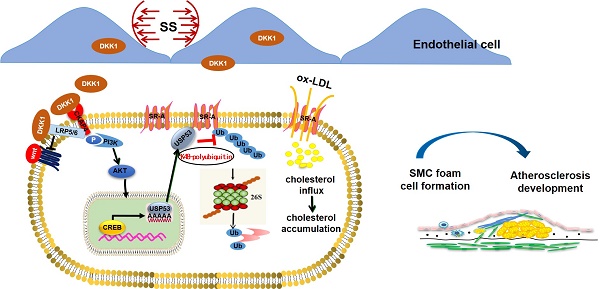
Background: Shear stress-induced Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) secretion by endothelial cells (ECs) promotes EC dysfunction and accelerates atherosclerosis (AS). However, the paracrine role of endothelial DKK1 in modulating adjacent smooth muscle cells (SMCs) in atherosclerosis remains unclear. This study investigated the role of EC-secreted DKK1 in SMC-derived foam cell formation under shear stress, in vitro and in vivo.
Methods: Parallel-plate co-culture flow system was used to explore the cellular communication between ECs and SMCs under shear stress in vitro. Endothelium-specific knockout of DKK1 (DKK1ECKO/APOE-/-) and endothelium-specific overexpression of DKK1 (DKK1ECTg) mice were constructed to investigate the role of endothelial DKK1 in atherosclerosis and SMC-derived foam cell formation in vivo. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was used to identify the downstream targets of DKK1. Reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), western blot, coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments were conducted to explore the underlying regulatory mechanisms.
Results: DKK1 is transcriptionally upregulated in ECs under conditions of low shear stress, but not in co-cultured SMCs. However, DKK1 protein in co-cultured SMCs is increased via uptake of low shear stress-induced endothelial DKK1, thereby promoting lipid uptake and foam cell formation in co-cultured SMCs via the post-translational upregulation of scavenger receptor-A (SR-A) verified in parallel-plate co-culture flow system, DKK1ECKO and DKK1ECTg mice. RNA sequencing revealed that DKK1-induced SR-A upregulation in SMCs is dependent on Ubiquitin-specific Protease 53 (USP53), which bound to SR-A via its USP domain and cysteine at position 41, exerting deubiquitination to maintain the stability of the SR-A protein by removing the K48 ubiquitin chain and preventing proteasomal pathway degradation, thereby mediating the effect of DKK1 on lipid uptake in SMCs. Moreover, DKK1 regulates the transcription of USP53 by facilitating the binding of transcription factor CREB to the USP53 promoter. SMC-specific overexpression of USP53 via adeno-associated virus serotype 2 vectors in DKK1ECKO/APOE-/- mice reversed the alleviation of atherosclerotic plaque burden, SR-A expression and lipid accumulation in SMCs within plaques resulting from DKK1 deficiency.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that, endothelial DKK1, induced by pathological low shear stress, acts as an intercellular mediator, promoted the foam cell formation of SMCs. These results suggest that targeted intervention with endothelial DKK1 may confer beneficial effects on atherosclerosis.
Keywords: shear stress, atherosclerosis, Dickkopf-1, cellular communication, foam cell

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact