ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(8):3185-3200. doi:10.7150/ijbs.96233 This issue Cite
Research Paper
m6A RNA methylation drives kidney fibrosis by upregulating β-catenin signaling
1. State Key Laboratory of Organ Failure Research, National Clinical Research Center of Kidney Disease, Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
2. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Renal Failure Research, Guangdong Provincial Institute of Nephrology, Guangzhou, China.
Abstract
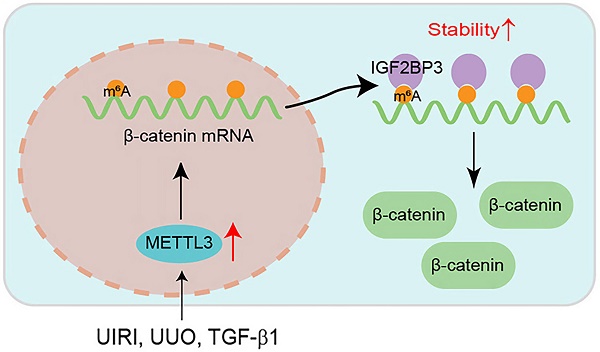
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methylation plays a crucial role in various biological processes and the pathogenesis of human diseases. However, its role and mechanism in kidney fibrosis remain elusive. In this study, we show that the overall level of m6A methylated RNA was upregulated and the m6A methyltransferase METTL3 was induced in kidney tubular epithelial cells in mouse models and human kidney biopsies of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Proximal tubule-specific knockout of METTL3 in mice protected kidneys against developing fibrotic lesions after injury. Conversely, overexpression of METTL3 aggravated kidney fibrosis in vivo. Through bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation, we identified β-catenin mRNA as a major target of METTL3-mediated m6A modification, which could be recognized by a specific m6A reader, the insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3). METTL3 stabilized β-catenin mRNA, increased β-catenin protein and induced its downstream profibrotic genes, whereas either knockdown of IGF2BP3 or inhibiting β-catenin signaling abolished its effects. Collectively, these results indicate that METTL3 promotes kidney fibrosis by stimulating the m6A modification of β-catenin mRNA, leading to its stabilization and its downstream profibrotic genes expression. Our findings suggest that targeting METTL3/IGF2BP3/β-catenin pathway may be a novel strategy for the treatment of fibrotic CKD.
Keywords: METTL3, m6A modification, β-catenin, IGF2BP3, kidney fibrosis, chronic kidney disease

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact