10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2024; 20(9):3269-3284. doi:10.7150/ijbs.96031 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Deubiquitination of CIB1 by USP14 promotes lenvatinib resistance via the PAK1-ERK1/2 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma
1. Department of Liver Surgery and Transplantation, Liver Cancer Institute and Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200032, China.
2. Institute of Fudan-Minhang Academic Health System, Minhang Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200032, China.
3. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Clinical Medical College, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, 225009, China.
4. Department of Digestive Medicine, Wuwei People's Hospital, Gansu, 733000, China.
5. Department of CT/MRI Center, Wuwei People's Hospital, Gansu, 733000, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
# Lead contact.
Abstract
Background: Lenvatinib is the most common multitarget receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Acquired resistance to lenvatinib is one of the major factors leading to the failure of HCC treatment, but the underlying mechanism has not been fully characterized.
Methods: We established lenvatinib-resistant cell lines, cell-derived xenografts (CDXs) and patient-derived xenografts (PDXs) and obtained lenvatinib-resistant HCC tumor tissues for further study.
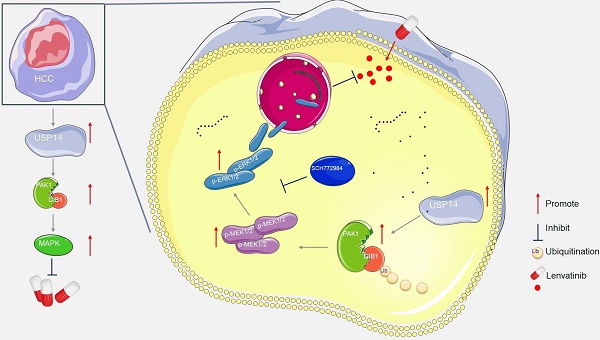
Results: We found that ubiquitin-specific protease 14 (USP14) was significantly increased in lenvatinib-resistant HCC cells and tumors. Silencing USP14 significantly attenuated lenvatinib resistance in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, USP14 directly interacts with and stabilizes calcium- and integrin-binding protein 1 (CIB1) by reversing K48-linked proteolytic ubiquitination at K24, thus facilitating the P21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1)-ERK1/2 signaling axis. Moreover, in vivo adeno-associated virus 9 mediated transduction of CIB1 promoted lenvatinib resistance in PDXs, whereas CIB1 knockdown resensitized the response of PDXs to lenvatinib.
Conclusions: These findings provide new insights into the role of CIB1/PAK1-ERK1/2 signaling in lenvatinib resistance in HCC. Targeting CIB1 and its pathways may be a novel pharmaceutical intervention for the treatment of lenvatinib-resistant HCC.
Keywords: USP14, HCC, CIB1, Lenvatinib resistance

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact